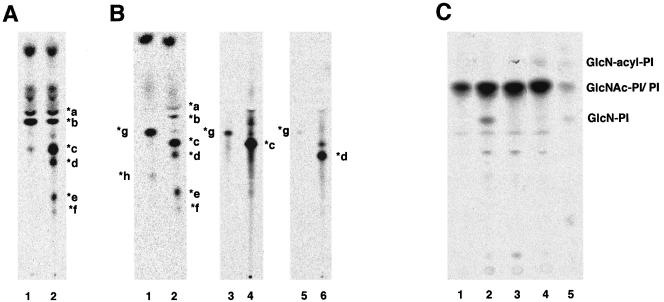
Figure 3.
Characterization of mannolipids accumulated in Molt4–1D10 (A and B) and analysis of early steps in GPI biosynthesis (C). (A) Molt4–1D10 cells cultured in the presence (lane 1) or absence (lane 2) of YW3548/BE49386A for 24 h were metabolically labeled with [3H]mannose. The lipids were analyzed by TLC with a solvent system of chloroform/methanol/H2O (10:10:3). (B) Molt4–1D10 cells were metabolically labeled with [3H]mannose. Lipids were treated with Jack bean α-mannosidase (lane 1) or buffer (lane 2), extracted again, and analyzed by TLC as described in A. Mannolipids *c and *d were eluted from the TLC plate (lanes 4 and 6) and treated with the α-mannosidase and reanalyzed by TLC (lanes 3 and 5). (C) Wild-type Molt4 (lane 1), 1D10 mutant (lane 2), 1D10 transfected with rat PIG-W cDNA (lane 3), and class E mutant (lane 4) cells were cultured in a medium containing myo-[3H]inositol for 1 d. The radiolabeled lipids were analyzed by TLC with a solvent system of chloroform/methanol/1 M NH4OH (10:10:3). Lane 5, standard GlcNAc-PI, GlcN-PI, and GlcN-acylPI generated by incubating membranes of wild-type Molt4 with UDP-[6-3H]GlcNAc. PI and GlcNAc-PI are overlapping.