Abstract
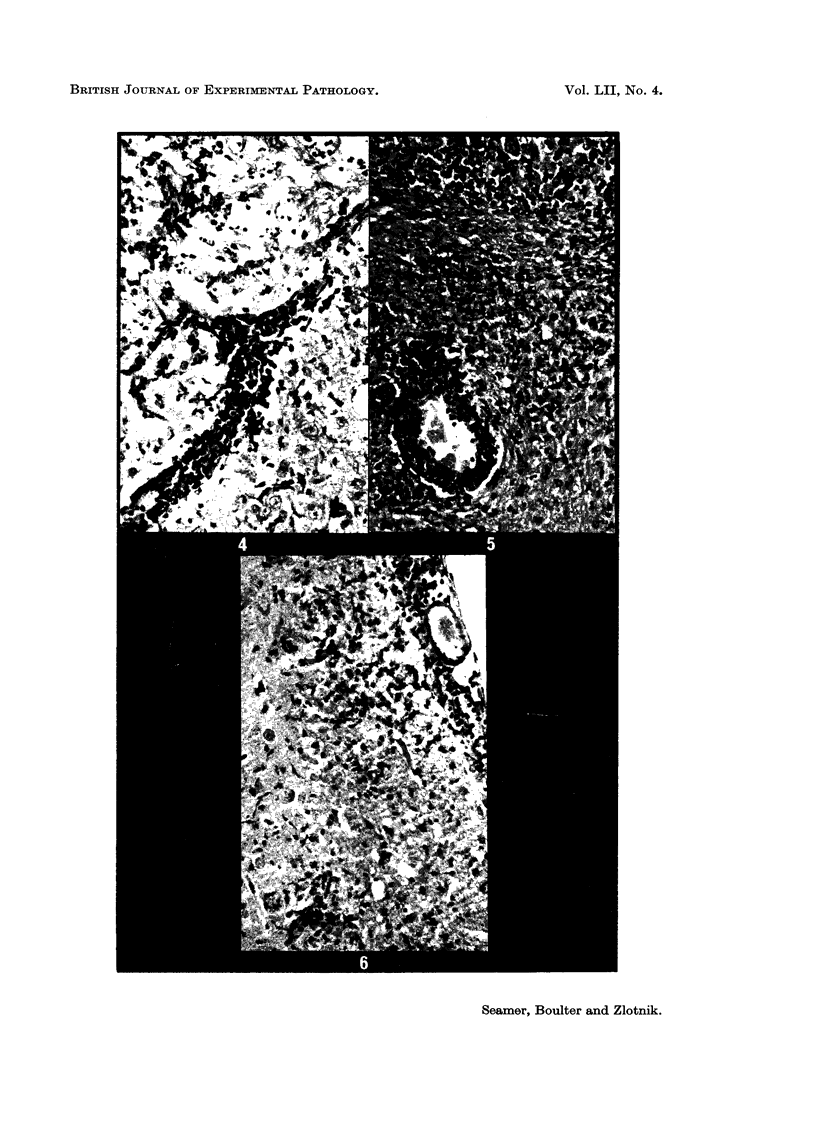
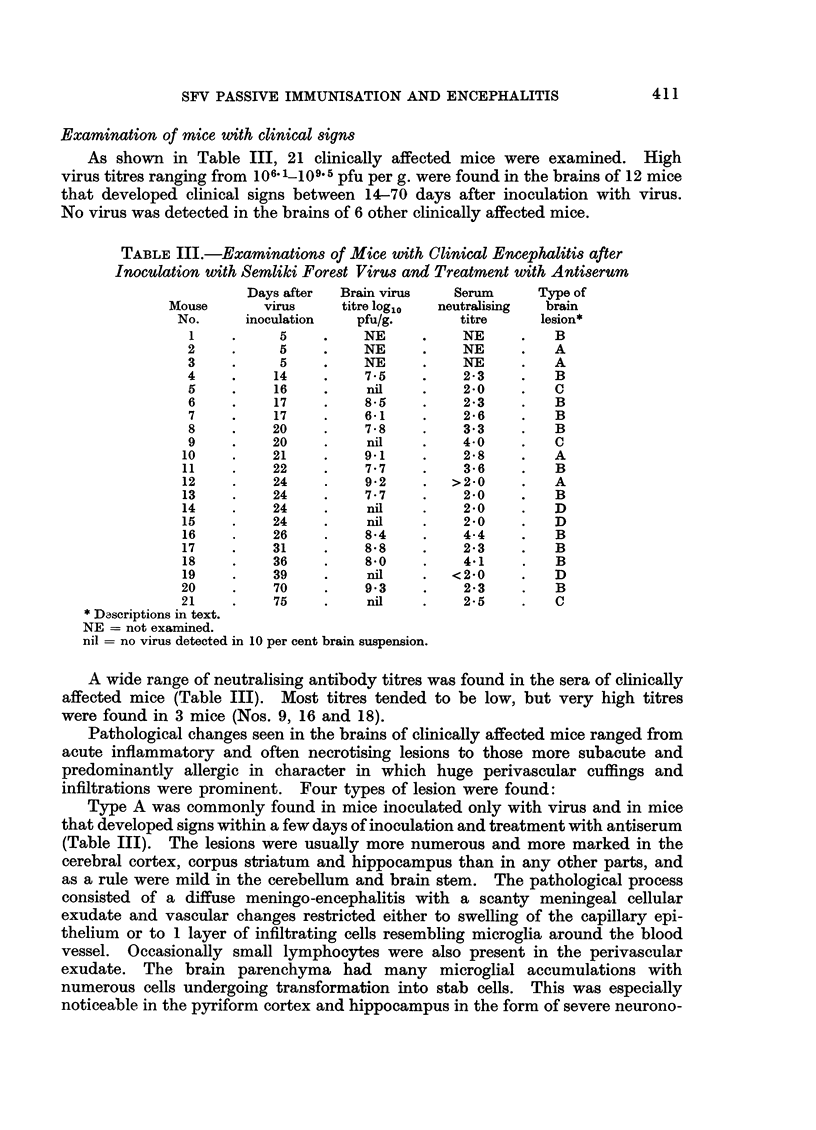
After a delay of 2 to 10 weeks or longer, clinical encephalitis developed in 15 per cent of mice which were protected against the acute stage of Semliki Forest virus (SFV) infection by antiserum. Some of these mice had high titres of SFV in their brains together with lesions of acute encephalitis while the others had subacute lesions and no virus was detected. When brains of apparently healthy mice which had survived the acute stage of SFV infection were examined, 90 per cent appeared to be histologically normal, but residual lesions of encephalitis were found in most of the remainder. Although no virus was detected in the brains of apparently healthy mice which survived the acute stage, the development of delayed encephalitis appeared to be due to persistence of SFV from the original infection. Examination of the sera of mice treated with antiserum suggested that most failed to develop active immunity.
Full text
PDF
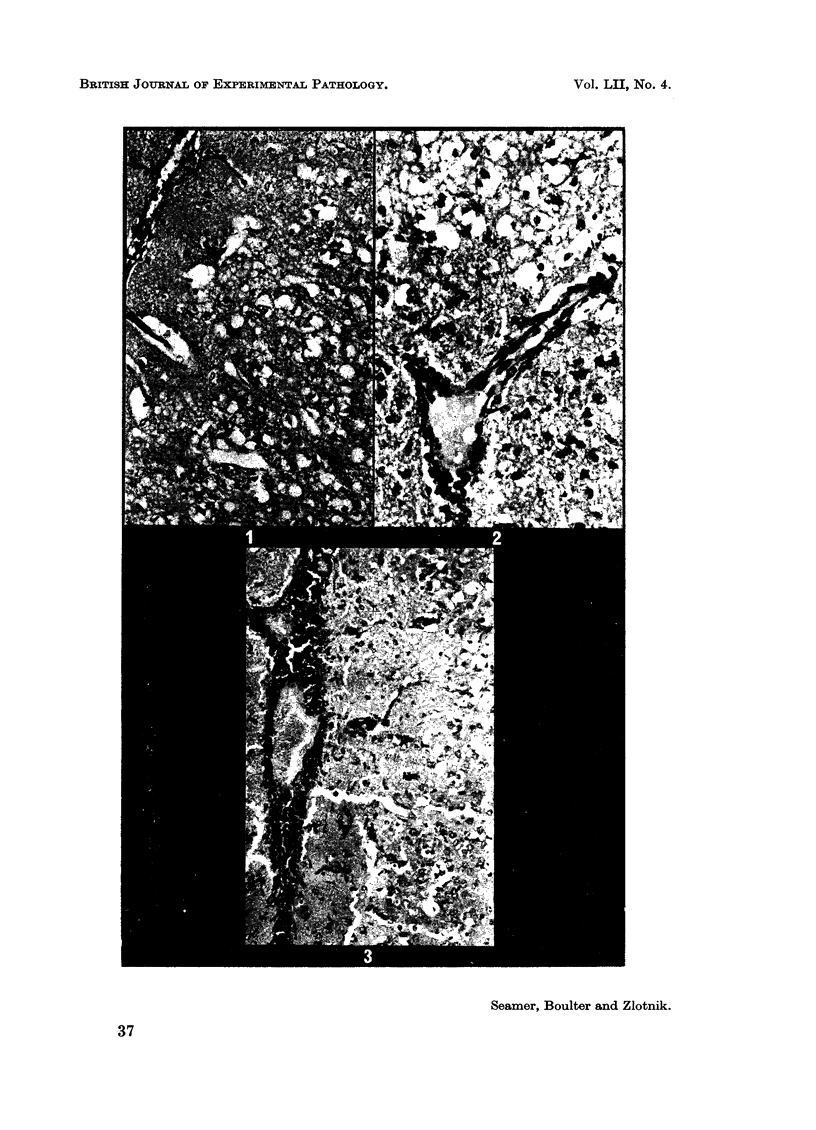






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGE T. O., GLEISER C. A., GOCHENOUR W. S., Jr, MIESSE M. L., TIGERTT W. D. Studies on the virus of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis. II. Modification by specific immune serum of response of central nervous system of mice. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:509–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette E. H., Magoffin R. L., Freeman J. M. Immunologic evidence of measles virus as an etiologic agent in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Neurology. 1968 Jan;18(1 Pt 2):21–29. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.1_part_2.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price W. H. Chronic disease and virus persistence in mice inoculated with Kyasanur forest disease virus. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):679–681. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamer J., Randles W. J., Fitzgeorge R. The course of Semliki Forest virus infection in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Aug;48(4):395–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb H. E., Wight D. G., Platt G. S., Smith C. E. Langat virus encephalitis in mice. I. The effect of the administration of specific antiserum. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Sep;66(3):343–354. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400041218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik I., Smith C. E., Grant D. P., Peacock S. The effect of immunosuppression on viral encephalitis, with special reference to cyclophosphamide. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Aug;51(4):434–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]