Abstract
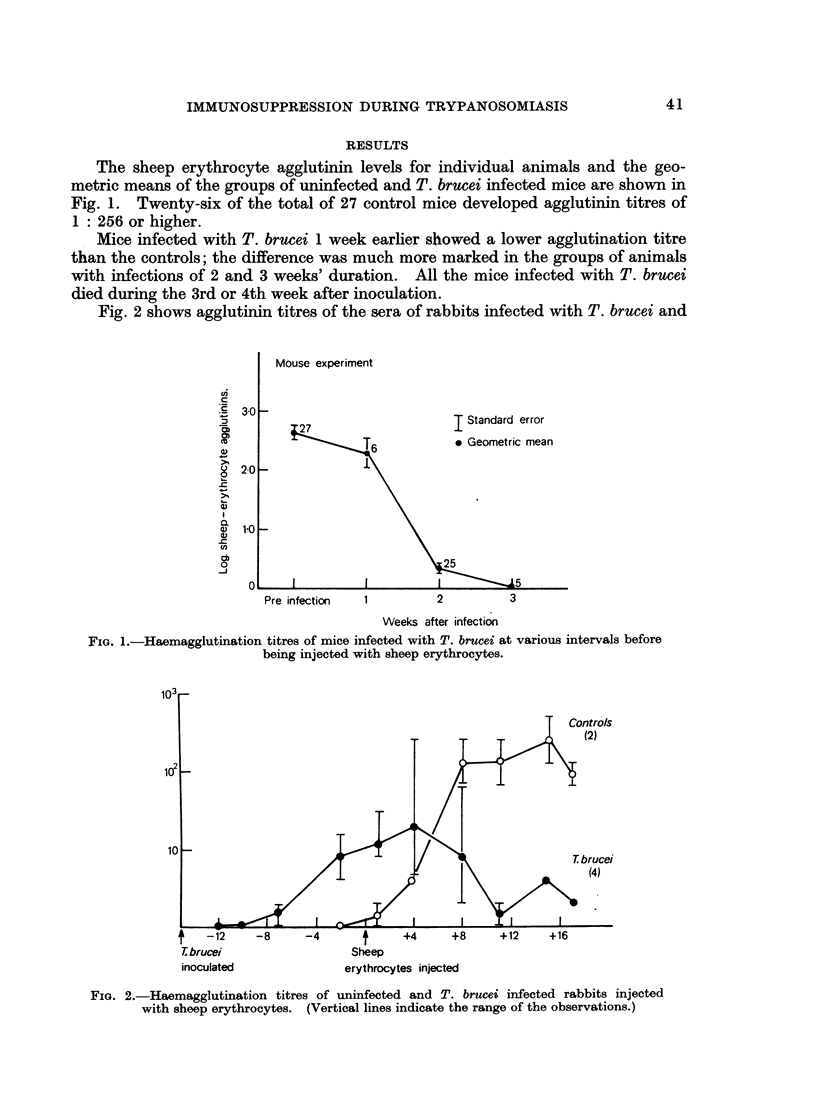
Mice and rabbits infected with Trypanosoma brucei developed much lower agglutinin levels than uninfected animals when injected with sheep erythrocytes. The immunosuppression became more marked as the infection progressed. The infected rabbits produced heterophile agglutinins but the mice did not.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allt G., Evans E. M., Evans D. H., Targett G. A. Effect of infection with trypanosomes on the development of experimental allergic neuritis in rabbits. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):197–199. doi: 10.1038/233197b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. R. Experimental malaria: effects upon the immune response to different antigens. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):99–101. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton B. A., Stauber L. A., Palczuk N. C. Leishmania donovani: antibody response to chicken ovalbumin by infected golden hamsters. Exp Parasitol. 1969 Aug;25(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(69)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin L. G. The pathology of African trypanosomiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970;64(6):797–817. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(70)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M. Autoimmune disease and parasitic infections in Nigerians. Lancet. 1968 Aug 17;2(7564):380–382. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Herrick E. M., Voller A. Can parasitic infection suppress autoimmune disease? Proc R Soc Med. 1970 Jan;63(1):19–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Playfair J. H., Torrigiani G. Immunosuppression in murine malaria. I. General characteristics. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Mar;8(3):467–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V., Allison A. C. M-antiglobulins (rheumatoid-factor-like globulins) and other gamma-globulins in relation to tropical parasitic infections. Lancet. 1966 Apr 16;1(7442):848–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V., Brown K. N., Allison A. C. Heterophile antibodies, M-antiglobulins and immunoglobulins in experimental trypanosomiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):113–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein F., Mattern P., Bosch HJ vd Experimental induction of rheumatoid factor-like substances in animal trypanosomiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Dec;7(6):851–863. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaman M. H., Wedderburn N., Bruce-Chwatt L. J. The immunodepressive effect of a murine plasmodium and its interaction with murine oncogenic viruses. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(3):383–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedderburn N. Effect of concurrent malarial infection on development of virus-induced lymphoma in Balb-c mice. Lancet. 1970 Nov 28;2(7683):1114–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


