Abstract
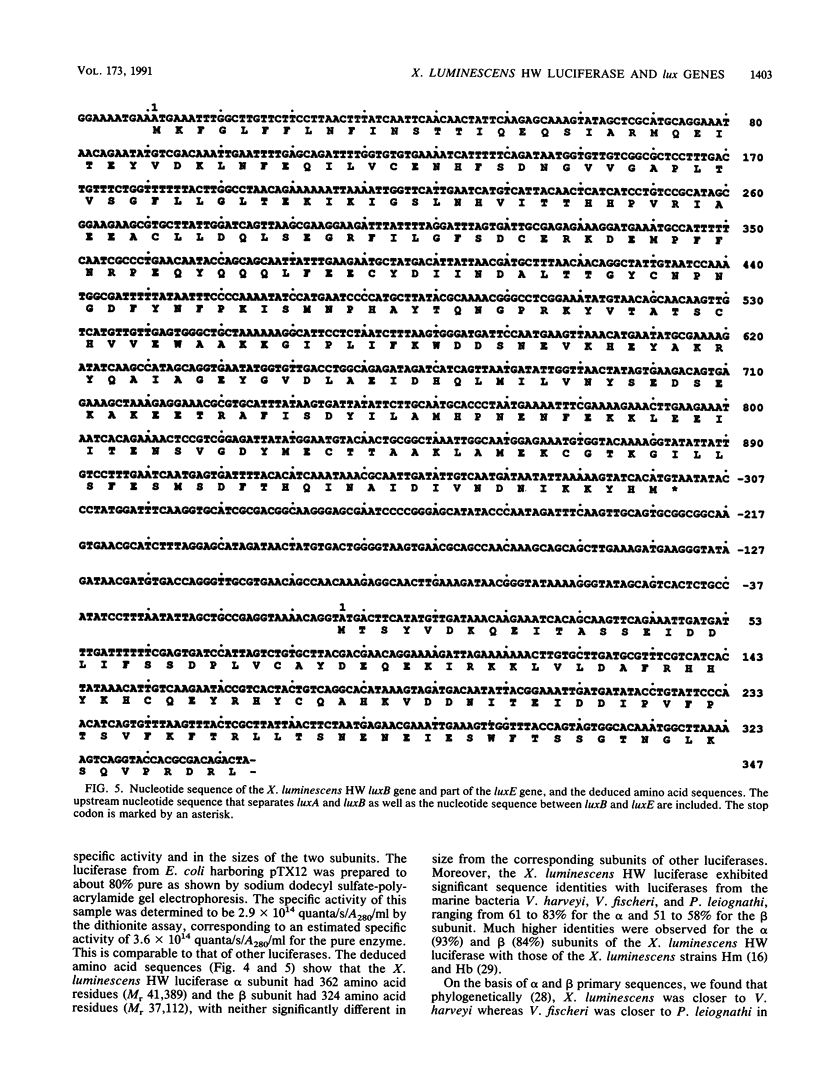
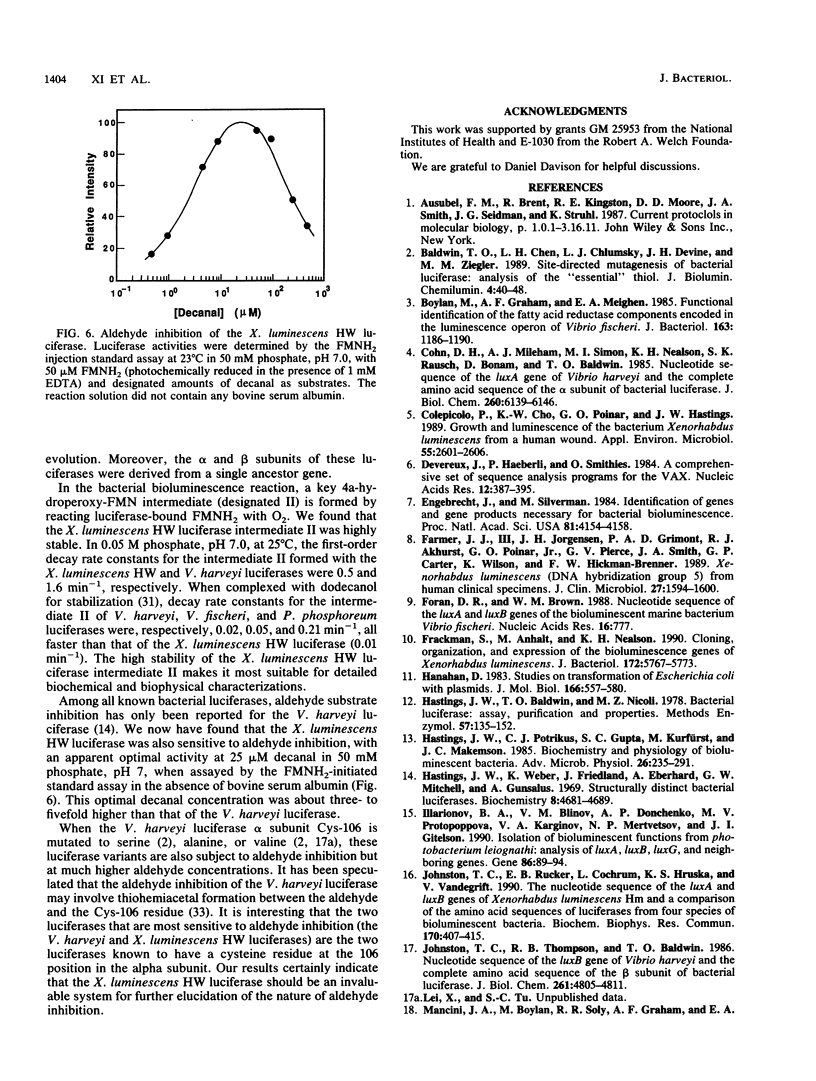
Xenorhabdus luminescens HW is the only known luminous bacterium isolated from a human (wound) source. A recombinant plasmid was constructed that contained the X. luminescens HW luxA and luxB genes, encoding the luciferase alpha and beta subunits, respectively, as well as luxC, luxD, and a portion of luxE. The nucleotide sequences of these lux genes, organized in the order luxCDABE, were determined, and overexpression of the cloned luciferase genes was achieved in Escherichia coli host cells. The cloned luciferase was indistinguishable from the wild-type enzyme in its in vitro bioluminescence kinetic properties. Contrary to an earlier report, our findings indicate that neither the specific activity nor the size of the alpha (362 amino acid residues, Mr 41,389) and beta (324 amino acid residues, Mr 37,112) subunits of the X. luminescens HW luciferase was unusual among known luminous bacterial systems. Significant sequence homologies of the alpha and beta subunits of the X. luminescens HW luciferase with those of other luminous bacteria were observed. However, the X. luminescens HW luciferase was unusual in the high stability of the 4a-hydroperoxyflavin intermediate and its sensitivity to aldehyde substrate inhibition.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. O., Chen L. H., Chlumsky L. J., Devine J. H., Ziegler M. M. Site-directed mutagenesis of bacterial luciferase: analysis of the 'essential' thiol. J Biolumin Chemilumin. 1989 Jul;4(1):40–48. doi: 10.1002/bio.1170040111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Functional identification of the fatty acid reductase components encoded in the luminescence operon of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Mileham A. J., Simon M. I., Nealson K. H., Rausch S. K., Bonam D., Baldwin T. O. Nucleotide sequence of the luxA gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6139–6146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colepicolo P., Cho K. W., Poinar G. O., Hastings J. W. Growth and luminescence of the bacterium Xenorhabdus luminescens from a human wound. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2601–2606. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2601-2606.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engebrecht J., Silverman M. Identification of genes and gene products necessary for bacterial bioluminescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4154–4158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Jorgensen J. H., Grimont P. A., Akhurst R. J., Poinar G. O., Jr, Ageron E., Pierce G. V., Smith J. A., Carter G. P., Wilson K. L. Xenorhabdus luminescens (DNA hybridization group 5) from human clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1594–1600. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1594-1600.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foran D. R., Brown W. M. Nucleotide sequence of the LuxA and LuxB genes of the bioluminescent marine bacterium Vibrio fischeri. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):777–777. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackman S., Anhalt M., Nealson K. H. Cloning, organization, and expression of the bioluminescence genes of Xenorhabdus luminescens. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5767–5773. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5767-5773.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Potrikus C. J., Gupta S. C., Kurfürst M., Makemson J. C. Biochemistry and physiology of bioluminescent bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1985;26:235–291. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Weber K., Friedland J., Eberhard A., Mitchell G. W., Gunsalus A. Structurally distinct bacterial luciferases. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4681–4689. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illarionov B. A., Blinov V. M., Donchenko A. P., Protopopova M. V., Karginov V. A., Mertvetsov N. P., Gitelson J. I. Isolation of bioluminescent functions from Photobacterium leiognathi: analysis of luxA, luxB, luxG and neighboring genes. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90117-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston T. C., Rucker E. B., Cochrum L., Hruska K. S., Vandegrift V. The nucleotide sequence of the luxA and luxB genes of Xenorhabdus luminescens HM and a comparison of the amino acid sequences of luciferases from four species of bioluminescent bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92106-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston T. C., Thompson R. B., Baldwin T. O. Nucleotide sequence of the luxB gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the beta subunit of bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4805–4811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini J. A., Boylan M., Soly R. R., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Cloning and expression of the Photobacterium phosphoreum luminescence system demonstrates a unique lux gene organization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14308–14314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Bartlet I. Complementation of subunits from different bacterial luciferases. Evidence for the role of the beta subunit in the bioluminescent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11181–11187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Hastings J. W. Binding site determination from kinetic data. Reduced flavin mononucleotide binding to bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7666–7674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C. M., Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Organization of the lux structural genes of Vibrio harveyi. Expression under the T7 bacteriophage promoter, mRNA analysis, and nucleotide sequence of the luxD gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13393–13399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Hastings J. W. Bacterial bioluminescence: its control and ecological significance. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):496–518. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.496-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Hastings J. W. Formation of hybrid luciferases from subunits of different species of Photobacterium. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):4989–4993. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., Kopecky K., Nealson K. H. Bioluminescence of the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus luminescens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2607–2612. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2607-2612.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szittner R., Meighen E. Nucleotide sequence, expression, and properties of luciferase coded by lux genes from a terrestrial bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16581–16587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu S. C. Isolation and properties of bacterial luciferase-oxygenated flavin intermediate complexed with long-chain alcohols. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 25;18(26):5940–5945. doi: 10.1021/bi00593a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu S., Hastings J. W. Differential effects of 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate upon binding of oxidized and reduced flavines by bacterial luciferase. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4310–4316. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


