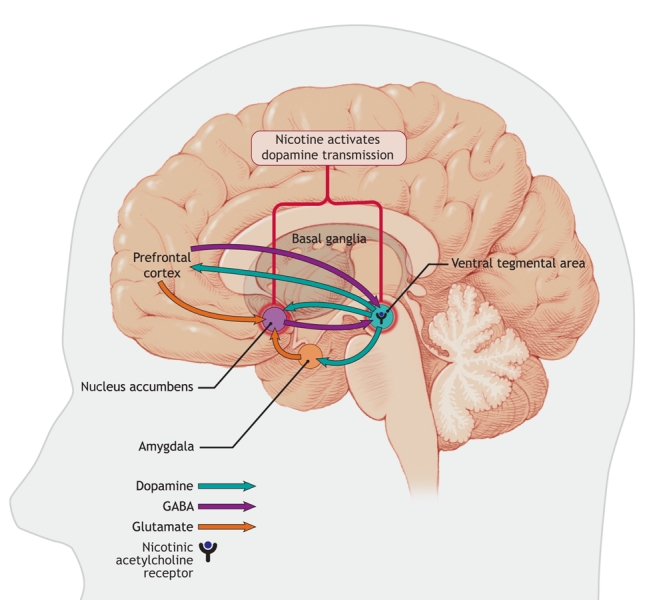
Figure 1: Areas in the brain involved in nicotine addiction. Nicotine stimulates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located in the ventral tegmental area, which leads to the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, an important step in the process of nicotine addiction. Neurons projecting from the prefrontal cortex and amygdala modulate the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, which allows for control of these addictive behaviours. These regulatory pathways are comprised of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons. Image by: Lianne Friesen and Nicholas Woolridge
