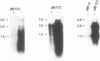Abstract
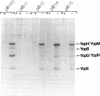
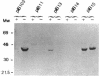
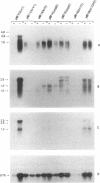
Virulent Yersinia species possess a common plasmid that encodes essential virulence determinants (Yops) which are regulated by the extracellular stimuli Ca2+ and temperature. The V antigen operon was recently shown to be involved in the Ca2(+)-regulated negative pathway (A. Forsberg and H. Wolf-Watz, Mol. Microbiol. 2:121-133, 1988). We show here that the V antigen-containing operon of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is a polycistronic operon having the gene order lcrGVH-yopBD. DNA sequencing analysis of lcrGVH revealed a high homology to the corresponding genes of Yersinia pestis. LcrG was conserved and LcrH showed only one amino acid difference, while LcrV showed only 96.6% identity. The amino acid substitutions of LcrV occurred in the central domain of the protein, while the two ends of the protein were conserved. Northern (RNA) blotting experiments showed that the operon is regulated at the transcriptional level by the extracellular stimuli temperature and calcium. One 4.6-kb transcriptional product of the operon was identified. This mRNA is rapidly processed at its 5' end, resulting in different mRNA species of variable stability. By genetic analysis, the lcrV and lcrH gene products were found to be regulatory proteins having important roles in the Ca2(+)-controlled regulation of Yop expression. The activity of LcrH is modulated by a gene product of the operon that inhibits the negative action of LcrH on yop transcription in the absence of Ca2+.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Fisher W. D., Cohen A., Hardigree A. A. MINIATURE escherichia coli CELLS DEFICIENT IN DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):321–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: an antigen determining virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Oct;37(5):481–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. V and W antigens in strains of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W. Genetics of virulence in bacteria. Br Med Bull. 1962 Jan;18:69–73. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barve S. S., Straley S. C. lcrR, a low-Ca2(+)-response locus with dual Ca2(+)-dependent functions in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4661–4671. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4661-4671.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The Vwa+ virulence factor of yersiniae: the molecular basis of the attendant nutritional requirement for Ca++. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S748–S758. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Båga M., Göransson M., Normark S., Uhlin B. E. Processed mRNA with differential stability in the regulation of E. coli pilin gene expression. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Forsberg A., Norlander L., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Identification and mapping of the temperature-inducible, plasmid-encoded proteins of Yersinia spp. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):343–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.343-348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. The plasmid-encoded Yop2b protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is a virulence determinant regulated by calcium and temperature at the level of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Mar;2(2):237–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Sluiters C., de Rouvroit C. L., Michiels T. Homology between virF, the transcriptional activator of the Yersinia virulence regulon, and AraC, the Escherichia coli arabinose operon regulator. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.254-262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Sory M. P., Laroche Y., Derclaye I. Genetic analysis of the plasmid region controlling virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica 0:9 by Mini-Mu insertions and lac gene fusions. Microb Pathog. 1986 Aug;1(4):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis G., Vanootegem J. C., Sluiters C. Transcription of the yop regulon from Y. enterocolitica requires trans acting pYV and chromosomal genes. Microb Pathog. 1987 May;2(5):367–379. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg A., Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Molecular cloning and expression of calcium-regulated, plasmid-coded proteins of Y. pseudotuberculosis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):123–137. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg A., Wolf-Watz H. Genetic analysis of the yopE region of Yersinia spp.: identification of a novel conserved locus, yerA, regulating yopE expression. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1547-1555.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg A., Wolf-Watz H. The virulence protein Yop5 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is regulated at transcriptional level by plasmid-plB1-encoded trans-acting elements controlled by temperature and calcium. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):121–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Yother J., Straley S. C. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.842-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., KUPFERBERG L. L., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. III. Effects of calcium ions on the growth of virulent and avirulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.317-321.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels T., Cornelis G. Nucleotide sequence and transcription analysis of yop51 from Yersinia enterocolitica W22703. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Kinross J. Conditional lethality of recA and recB derivatives of a strain of Escherichia coli K-12 with a temperature-sensitive deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase I. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):971–978. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.971-978.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder B., Michiels T., Simonet M., Sory M. P., Cornelis G. Identification of additional virulence determinants on the pYV plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica W227. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2534–2541. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2534-2541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.166-171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Harmon P. A., Bowmer W. S., Straley S. C. A low-Ca2+ response operon encodes the V antigen of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.428-434.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. B., Leung K. Y., Barve S. S., Straley S. C. Molecular analysis of lcrGVH, the V antigen operon of Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5646–5653. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5646-5653.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. B., Straley S. C. lcrH, a gene necessary for virulence of Yersinia pestis and for the normal response of Y. pestis to ATP and calcium. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1491-1498.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Inhibition of phagocytosis in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: a virulence plasmid-encoded ability involving the Yop2b protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2139–2143. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2139-2143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Forsberg A., Rimpiläinen M., Bergman T., Wolf-Watz H. The cytotoxic protein YopE of Yersinia obstructs the primary host defence. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):657–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosqvist R., Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Increased virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by two independent mutations. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):522–524. doi: 10.1038/334522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Wolf-Watz H. Analysis of the yopA gene encoding the Yop1 virulence determinants of Yersinia spp. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):517–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Bowmer W. S. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):445–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.445-454.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Portnoy D. A., Bölin I., Falkow S. Transfer of the virulence plasmid of Yersinia pestis to Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):241–243. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.241-243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]