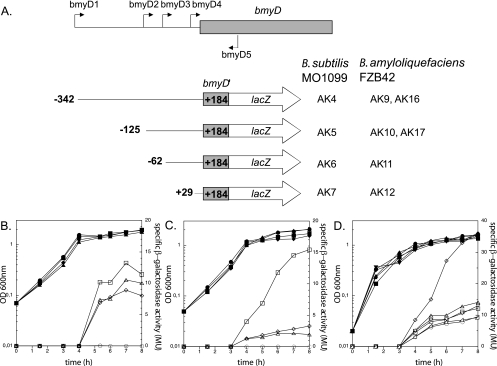
FIG. 2.
Mapping of the bmyD promoter region by 5′ deletions. (A) Schematic representation of the different bmyD::lacZ fusions used in this study. The filled arrows indicate the primers used for generating the various reporter fusions (bmyD1 to -D5), whereas the 5′ and 3′ end termini of the bmyD::lacZ fusions are denoted with their nucleotide position relative to the transcriptional start. The derivative B. subtilis MO1099 and FZB42 strains that carry the respective fusions are shown on the right (see Table 1). (B and C) Expression of the series of bmyD::lacZ fusions, with different 5′ end termini, in B. subtilis MO1099 (B) and in FZB42 (C). Cells were grown in Difco medium at 37°C, and optical densities (OD) (closed symbols) and β-galactosidase activities (open symbols) were determined during growth. Squares, strains AK4/AK9; diamonds, strains AK5/AK10; triangles, strains AK6/AK11; circles, strains AK7/AK12. (D) Effect of DegQ on the expression patterns of the various bmyD::lacZ fusions in B. subtilis MO1099. Squares, strain AK4 without plasmid; circles, strain AK5 without plasmid; diamonds, strain AK60 (AK4+pAK64) with plasmid induced; triangles facing down, strain AK60 with plasmid uninduced; triangles facing up, strain AK61 (AK5+pAK64) with plasmid induced; rectangle-triangles, strain AK61 with plasmid uninduced.