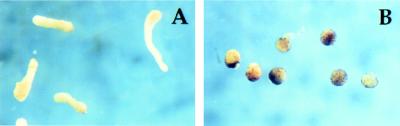
Figure 4.
Expression of K229 ventralizes dorsal mesoderm. (A and B) Animal caps explanted from stage 8 embryos injected at one-cell stage with 1 ng of control KALL mRNA (A) or K229 mRNA (B) were treated with 30 ng/ml activin. Photographs were taken after 8 h of culture. (C and D) Induction of mesodermal marker genes by activin in animal caps expressing various Nck clones. mRNA indicated above lanes was injected as in A and B, and animal caps explanted at stage 8. In XK229(0.25) and K229(0.25) lanes, 0.25 ng of RNA was injected, all others 1 ng. XK229 indicates K229 mutant of Xenopus Nck gene; all other constructs were derived from human gene. K229(−), XK229(−), unij(−): K229- or XK229-injected or uninjected control caps without activin treatment. WE, whole embryo. EF1α is control for template levels in RT–PCR. Results shown are representative of three experiments. (C) After 2-h incubation with activin at 100 ng/ml, animal caps were harvested for RT–PCR at stage 11. (Bottom) Injected embryos were cultured until stage 12 for examination of Nck protein expression levels by immunoblot. (D) Animal caps treated with 5 ng/ml activin for 2 h and harvested for RT–PCR at stage 36. (E and F) Induction of mesodermal marker genes in DMZ explants. mRNA indicated above lanes was injected into dorsal blastomeres of 4-cell embryos (0.5 ng/blastomere). DMZ explants from early gastrula embryos were cultured until harvested for RT–PCR at stage 12 (E) or stage 19 (F). KALL, RT(−); KALL-injected control reaction lacking RT.