Figure 7. Chemical characteristics of vas deferens autonomic innervation in adult control and hpg mice.
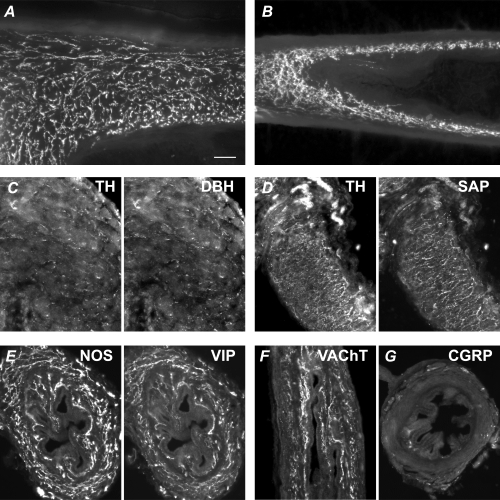
A and B, numerous axons in the muscle show catecholamine histofluorescence (glyoxylic acid method) in the control (A) and hpg (B) vas deferens. Panels C–G show vasa from hpg mice. Panels A, B, D and F show vasa sectioned longitudinally and panels C, E and G are transverse sections. C, TH-immunoreactive axons coexpress dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH). D, TH-immunoreactive axons coexpress the synaptic protein, synapsin (SAP). E, NOS-immunoreactive axons coexpress vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). F, vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT)-immunoreactive axons are prevalent in the muscle and mucosa. G, sensory fibres immunolabelled for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) are rare in the muscle and mucosa, but nerve bundles can be seen in the serosa. Calibration bar represents 50 μm in all micrographs except C (20 μm).
