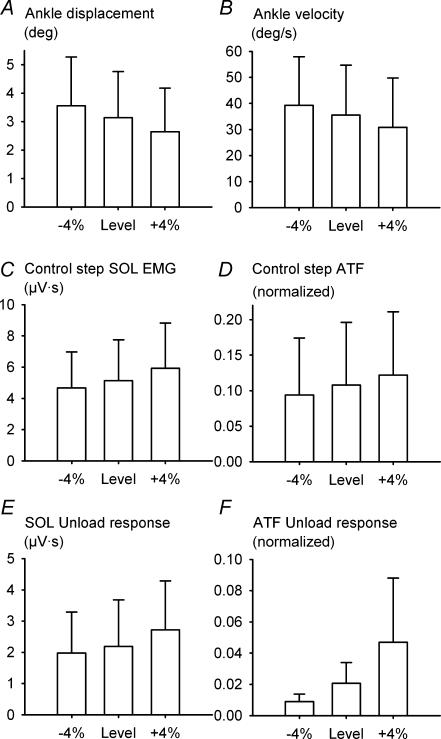
Figure 2. The effect of treadmill inclination on the control step ankle angular displacement (A), ankle angular velocity (B), control step soleus EMG (C), normalized Achilles' tendon force (D), soleus unload response (E) and Achilles' tendon unload response (F).
Data are illustrated as mean ± s.d. across all 21 subjects (8 subjects for ATF). Ankle displacement and velocity decrease with treadmill inclination (P < 0.001 in both cases). In contrast, the control step soleus EMG, normalized control step Achilles' tendon force, soleus unload response, and normalized Achilles' tendon force unload response increase with treadmill inclination (P < 0.001, P < 0.006, P < 0.001 and P = 0.026, respectively).