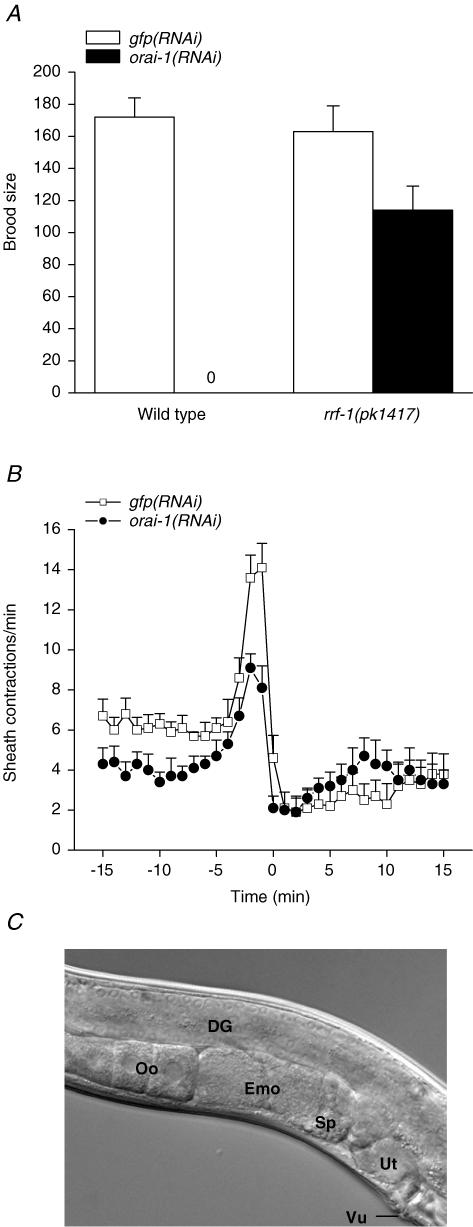
Figure 3. Effect of orai-1 RNAi on fertility and ovulation.
A, brood size in wild-type and rrf-1(pk1417) mutant worms. Brood size is defined as the total number of progeny produced over four days. rrf-1 encodes an RNA-directed RNA polymerase homologue required for RNAi in somatic but not germ cells. pk1417 is a predicted rrf-1 null allele (Sijen et al. 2001). Worms were fed GFP or orai-1 dsRNA-producing bacteria for two generations beginning at the L1 larval stage. Values are means ± s.e.m. (n = 6–12). B, rates of sheath contraction during a single ovulatory cycle. Time 0 is defined as the time at which ovulation was completed in control worms. orai-1(RNAi) worms never ovulated (see Results). Therefore in these animals, time 0 is defined the first time point after peak sheath contraction rate was observed. Values are means ± s.e.m. (n = 6–7). Worms were fed dsRNA-producing bacteria for two generations. C, differential interference contrast micrograph of the gonad of an orai-1(RNAi) worm. The distal spermatheca fails to open during ovulation in orai-1(RNAi) worms, and oocytes are trapped in the proximal gonad arm where they undergo endomitosis. DG, Distal gonad; Oo, normal oocytes; Emo, endomitotic oocytes; Sp, spermatheca; Ut, uterus; Vu, vulva. Note that the uterus in the orai-1(RNAi) worm is empty due to failure of ovulation. worms fed dsRNA-producing bacteria for two generations.