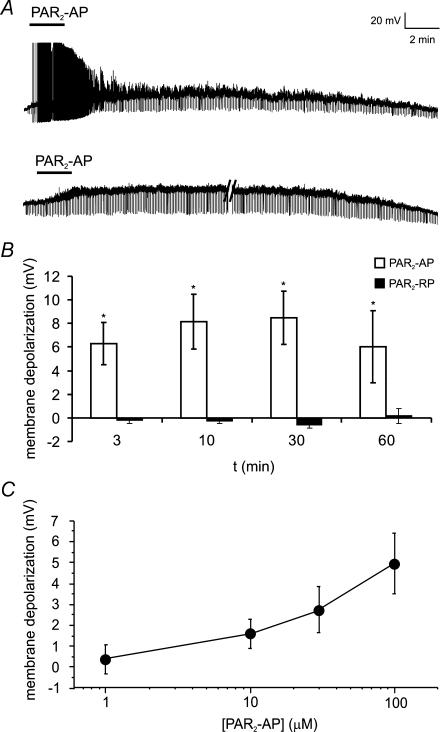
Figure 2. PAR2-AP evokes sustained depolarization of mouse colonic DRG neurons.
A, representative traces showing PAR2-AP (SLIGRL; 100 μm) superfusion for 3 min caused a sustained depolarization of mouse DRG neurons for up to 60 min. This was associated with action potential discharge in a few neurons (upper trace) and an increase in input resistance (brief downward deflections evoked by constant hyperpolarizing pulse). Parallel lines (lower trace) represent 16 min break in recording. Each neuron was recorded for 5 min prior to application of the PAR2-AP (not shown) to ensure a stable resting membrane potential. B, summary of mean depolarization at each time point following superfusion of PAR2-AP (100 μm). The reverse peptide, which lacks biological activity at the PAR2 (PAR2-RP, LRGILS; 100 μm), had no effect on membrane potential. n = 5 or more for each time point. C, PAR2-AP (1–100 μm) evoked a dose-dependent depolarization. n = 5 or more neurons at each point.