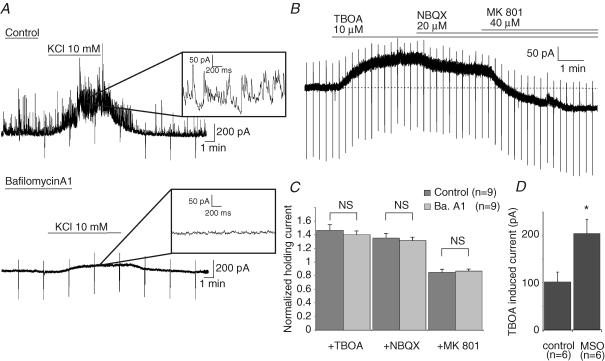
Figure 4. Glial origin of the ambient glutamate mediating the tonic activation of NMDARs.
A, the frequency of the synaptic currents recorded in a pyramidal neuron in a control slice bathed in normal extracellular solution was greatly enhanced by the application of 10 mm KCl (top). Pre-incubating the slices with the H+-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 (4 μm, 2.5 h, 34°C) inhibited spontaneous and KCl-evoked synaptic currents (bottom). Insets show a portion of each recording at a faster time scale. B, the trace shows the effect of TBOA (100 μm), NBQX (20 μm) and MK801 (40 μm) on the tonic current of a pyramidal neuron recorded in bafilomycin A1-treated slice. C, the histogram shows that the effects of TBOA, NBQX and MK801 do not differ significantly between control (dark grey bars) and bafilomycin A1-treated slices (light grey bars). Values of the tonic currents are normalized to the amplitude of the baseline holding current (i.e. before the application of TBOA). D, incubation of the slices in presence of the glutamine synthase inhibitor l-methionine sulfoximine (MSO, 5 mm, 1–3 h, 34°C) increased the TBOA-induced current.