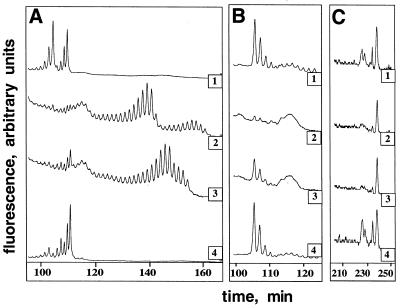
Figure 3.
Display of different HD alleles from three related individuals (traces: 1, HD-A; 2, HD-B; and 3, HD-C) and an anonymous unrelated control (trace 4) in a Sau96 I CAG-containing genome subset. Because there were many differences between samples, a number of control experiments was done to determine the size of the HD alleles, to identify HD-containing fragments, and to understand the primary structure of the PCR products using different primers. A subset of these control experiments is shown in A and B, whereas the true HD genomic display is shown in C. (A) HD-specific amplification of genomic DNA using primers 9 (fluorescein-labeled) and 12 (Table 1) measured the size of the HD alleles. (B) The HD fragments, generated from genomic DNA using primers 11 and 12 (Table 1 and Fig. 2A), were digested with Sau96 I, tagged with Sau96 I adapters, and amplified by PCR using primer 5 and fluorescein-labeled CTG-repeat primer 13 (Table 1). This experiment measured the size of the HD-containing fragments when the PCR used adapter and repeat primers. (C) Genomic DNAs were digested with the restriction enzyme Sau96 I, ligated to adapter oligonucleotides of known sequence, and hybridized to a (CAG)12-containing oligonucleotide probe. The captured fragments were amplified by PCR using CAG repeat-containing primer 14 and fluorescein-labeled primer 5 (Table 1). This experiment displays Sau96 I CAG-containing genome subsets en masse. The differentially displayed fragments eluting at ≈227 min hybridized to an HD-specific capture probe (data not shown). Also not shown are the results of experiments using adapter primers only. These experiments detected the same differentially displayed fragments eluting at ≈227 min as shown in C.