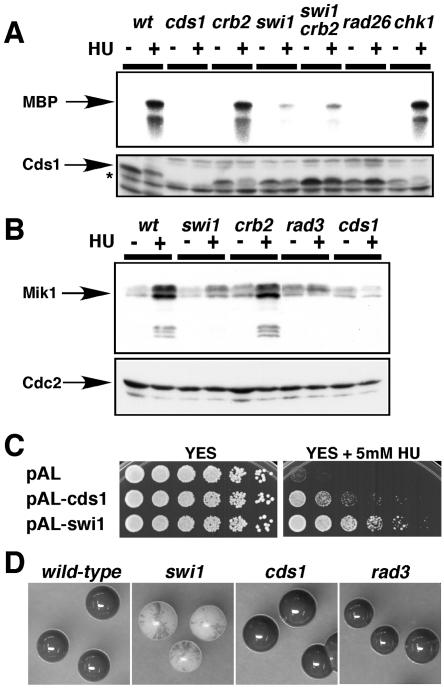
FIG. 3.
Deficient Cds1 activation in swi1 mutant. (A) Cds1 activation is strongly reduced in swi1 mutant cells. Cells of the indicated genotypes were incubated in YES liquid medium supplemented with 0 or 12 mM HU for 4 h at 30°C. Kinase activity of immunoprecipitated Cds1 was measured by using myelin basic protein (MBP) substrate (upper panel). A Cds1 immunoblot confirmed that approximately equal amounts of Cds1 (absent in cds1 mutant strain) were present in the samples (lower panel). The Cds1 polyclonal antisera cross-react with nonspecific proteins that migrate faster than Cds1 (asterisk). (B) HU induction of Mik1 accumulation is deficient in swi1 mutant cells. Cells of the indicated genotypes that contained genomic mik1-13myc were incubated with 0 or 12 mM HU for 4 h at 30°C. Mik1 was detected with anti-Myc monoclonal antibody (upper panel). A Cdc2 immunoblot was used as a loading control (lower panel). (C) HU sensitivity of swi1 mutant cells was partially suppressed by multicopy cds1+ plasmid. Fivefold serial dilutions of swi1 mutant cells transformed with the indicated plasmids were incubated on YES agar medium supplemented with the indicated amount of HU for 2 to 5 days at 30°C. (D) Colonies of homothallic wild-type and swi1, cds1, and rad3 mutant cells were grown in sporulation medium and then stained by iodine vapor to detect spores. The swi1 mutant colonies showed a mottled phenotype, indicating a defect in mating type switching, whereas wild-type and cds1 and rad3 mutant cells stained darkly with iodine, indicating proficient mating type switching.