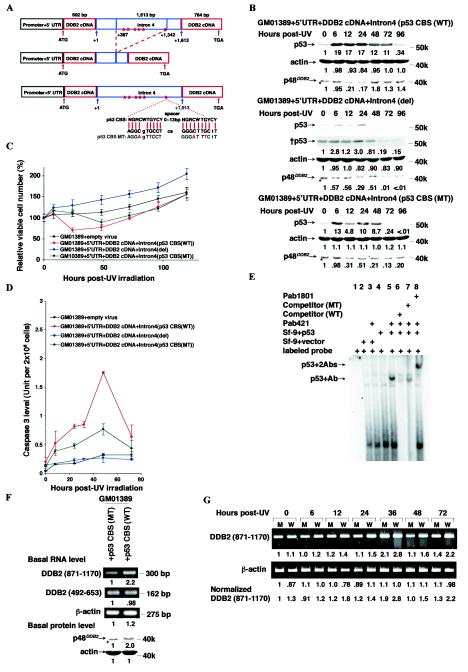
FIG.6.
Intron 4, including the p53 CBS of the DDB2 gene, is important for controlling levels of DDB2 RNA, p48DDB2, and p53, and apoptosis. (A) Graphic representation of mutant DDB2 constructs. Both constructs were made from the DDB2 construct including the wild-type intron 4. For the deletion mutant, a 955-bp fragment (+387 to + 1342) of intron 4 (+1 is a first nucleotide of intron 4) was removed. For the p53 CBS mutant, 4 nucleotides were changed to alter both elements of the p53 CBSs. (B) Protein levels before and after 12 J of UV irradiation m−2 in the XP-E strain GM01389 with the mutant DDB2 constructs. The construct with the wild-type p53 CBS was used as a control. The exposure times were 30 s (p53), 2 min (†p53), 15 s (p21CDKN1A), 1 min (†p21CDKN1A), 20 min (p48DDB2), 40 min (†p48DDB2), or 10 s (actin). The band marked with an asterisk lying just below p48DDB2 is nonspecific. Each basal protein level (0 h) was designated as 1.0 to compare protein levels during the time course. (C) Cell viability of XP-E strains harboring retroviral constructs used in panel B after 12 J of UV irradiation m−2. Viable cell number was determined by dye exclusion. Within an experiment, each point was determined in triplicate and each curve represents at least two such independent experiments, except that for 5′UTR+DDB2 cDNA+Intron 4 [p53 CBS (MT)] the experiment was performed once. (D) Caspase 3 activity of XP-E strains harboring retroviral constructs used in panel B after 12 J of UV irradiation m−2. Within an experiment, each point was determined in duplicate, and each curve represents at least two such independent experiments, except that for 5′UTR+DDB2 cDNA+Intron4 [p53 CBS (MT)], the experiment was performed once. (E) Mobility shift assays with p53 and a probe harboring the p53 CBS found in intron 4 of the DDB2 gene. 32P-labeled 34-bp oligonucleotides containing the wild-type or mutated p53 CBS as shown in panel A were incubated with extracts from Sf-9 cells infected with empty or p53 cDNA-containing viruses, anti-p53 antibodies, and unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides as indicated. Unbound labeled oligonucleotides were run off of the gel. p53+Ab, a band observed only when p53 and Pab421 are present; p53 + 2Abs, a band observed only when p53, Pab421, and Pab1801 are present. (F) Basal DDB2 and β-actin RNA and p48DDB2 and β-actin protein levels in the XP-E GM01389 strain with the DDB2 constructs with the wild-type (WT) or mutant (MT) p53 CBS. Each of RNA or protein levels was determined by semiquantitative RT-PCR or immunoblotting, respectively. The exposure times for immunoblotting were 20 min (p48DDB2) and 10 s (actin). The band marked with an asterisk lying just below p48DDB2 is nonspecific. Each protein level from cells infected with p53 CBS (MT) was designated as 1.0, and the respective levels of these proteins in p53 CBS (WT) were normalized accordingly. (G) Semiquantitative RT-PCR of DDB2 and β-actin in the XP-E GM01389 strain with the DDB2 constructs with the wild-type or mutant p53 CBS before and after 12 J of UV irradiation m−2. M, DDB2 construct with the mutant p53 CBS; W, DDB2 construct with the wild-type p53 CBS.