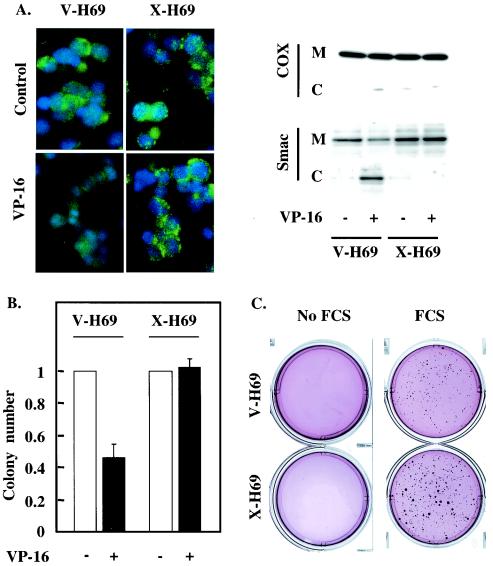
FIG. 6.
XIAP expression prevents Smac release and cell death in response to etoposide. (A and B) X-H69 and V-H69 were incubated with or without etoposide. (A) Smac localization was probed by using immunofluorescent staining (left) and cell fractionation (right). (Left) Smac immunoreactivity was revealed using an FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (green). Nuclear DNA was stained using DAPI (blue). (Right) Mitochondrial (M) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting for the presence of Smac. The absence of mitochondrial contamination of the cytoplasmic fraction was confirmed by detection of cytochrome oxidase (COX). (B) Cells were subjected to a clonogenic assay, and colony numbers were determined under microscopic observation. Error bars, standard errors of the means. (C) X-H69 and V-H69 were subjected to a clonogenic assay in the presence or absence of 10% FCS. The colonies were stained using nitroblue tetrazolium, and the plates were photographed. Each result is representative of three independent experiments (A through C) performed in triplicate (B and C).