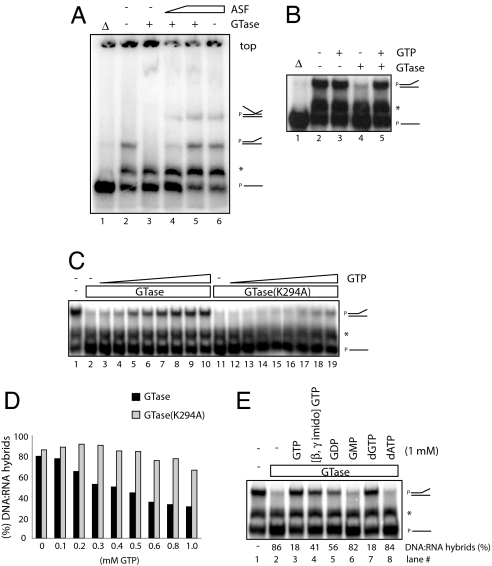
Fig. 4.
Characterization of CE-dependent RLF. (A) ASF/SF2 prevents CE-dependent RLF. RLF assays were performed with 200 ng of hGTase in the presence of increasing amounts (0, 70, and 140 ng) of ASF/SF2 (lanes 3–5). The effect of 140 ng of ASF-SF2 alone is shown in lane 6. Putative triplet structures containing all three nucleic acid strands correspond to the lowest mobility products. (B) GTP inhibits CE-dependent RLF. RLF assays were performed with 200 ng of wild-type GTase alone (lane 4) or plus 1 mM GTP (lane 5); 1 mM GTP alone is shown in lane 3. (C) Wild-type, but not mutant, GTase is a target for GTP-mediated inhibition of RLF. RLF assays were performed with 200 ng of hGTase (lanes 2–10) or hGTaseK294A (lanes 11–19) in the presence of increasing amounts (0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 mM) of GTP. (D) Quantitation of DNA·RNA hybrids shown in C. The amounts of DNA·RNA hybrids caused by CE were quantitated by the ratio of hybridized template strands in the presence or absence of hGTase. (E) (Upper) RLF assays with 200 ng of hGTase plus 1 mM GTP, β,γ-imido-GTP, GDP, GMP, dGTP, and dATP were examined. (Lower) Quatitations of RLF are shown.