Fig. 1.
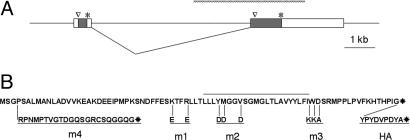
The inaF transcript and its coding potential. (A) Diagram of genomic DNA from the region of the inaF message. Two exons are shown that are spliced to make an abundant eye-enriched 3.1-kb transcript. The second exon contains an ORF whose first methionine and stop codon are, respectively, indicated by a caret and asterisk; this 241-aa polypeptide has been proposed to be the CG2457 gene product (5, 6). However, the first exon contains an 81-aa ORF that we show herein to be necessary and sufficient for inaF function. The hatched bar above the exon/intron diagram shows the extent of the P106x deletion (5) that inactivates the gene. (B) Sequence of the 81-aa protein. The overlined region marks a predicted membrane-spanning domain that runs from Leu-42 to Ile-63. Below the sequence are given the amino acid changes for three substitution mutants (m1–m3), a frameshift mutant (m4), and the additional amino acids that are appended to the C terminus to generate a tag (HA).