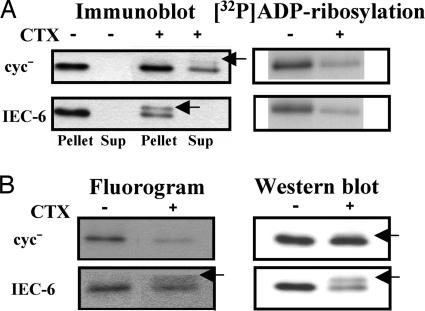
Fig. 5.
Effects of activation by cholera toxin (CTX) on the localization (A) and palmitoylation (B) of recombinant αs proteins in cyc− or IEC-6 cells expressing HA-tagged αs-WT. (A) cyc− (1.0 × 107) or IEC-6 (0.5 × 107) cells derived from 10-ml culture volumes were fractionated, and HA-tagged αs proteins were detected by immunoblotting with monoclonal antibody 12CA5 after immunoprecipitation with the same antibody. Membrane fractions of these cells were also prepared in which the αs was [32P]ADP-ribosylated with a 50 μg/ml concentration of activated cholera toxin. [32P]ADP-ribosylated HA-tagged αs proteins were then visualized by autoradiography after immunoprecipitation as described in Materials and Methods. Before fractionation, the cells were incubated without or with 1 μg/ml cholera toxin for 4 h. (B) cyc− (5.0 × 107) or IEC-6 (2.5 × 107) cells derived from 50-ml culture volumes were incubated for 2 h in DMEM containing 10% dialyzed FBS, 5 mM sodium pyruvate, and 0.5 mCi/ml [9,10-3H]palmitic acid. After labeling, the cells were incubated without or with cholera toxin for 4 h and fractionated. Palmitoylated HA-tagged αs proteins were visualized by fluorography (30-day exposure), and HA-tagged αs proteins were detected by immunoblotting after immunoprecipitation as described in Materials and Methods. Arrows indicate αs proteins that have been ADP-ribosylated by cholera toxin. Each set of results is representative of at least two additional experiments.