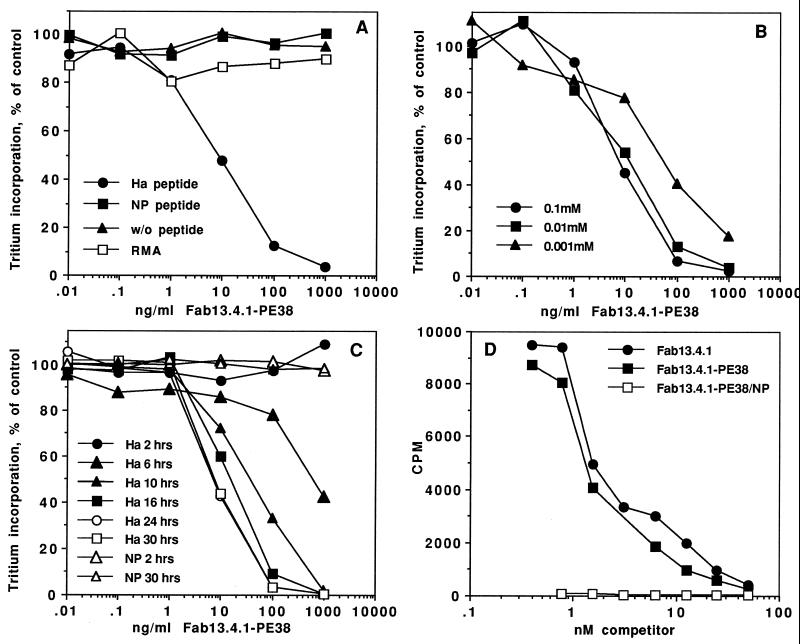
Figure 2.
Cytotoxicity and binding of Fab 13.4.1–PE38 to APCs. (A) Cytotoxic activity of recombinant Fab 13.4.1–PE38 to RMA-S⋅Kk cells with and without influenza peptides. RMA-S⋅Kk cells were incubated with 0.1 mM Ha and NP peptides at 26°C. Cells were then incubated for 20 hr with recombinant Fab 13.4.1–PE38. Protein synthesis is measured by incorporation of [3H]leucine into cell proteins. RMA cells are control cells that are the parental cells used to derive RMA-S⋅Kk. (B) Peptide titration for Fab 13.4.1–PE38 mediated cytotoxicity. RMA-S⋅Kk cells were incubated with various concentration of Ha peptide at 26°C. Cells were than exposed to Fab 13.4.1–PE38, and inhibition of protein synthesis was determined. (C) Kinetics of Fab 13.4.1–PE38 cytotoxic activity on RMA-S⋅Kk cells. RMA-S⋅Kk cells were incubated overnight with 0.1 mM Ha or NP peptide for the indicated times at 26°C. Cells were then exposed to Fab 13.4.1–PE38 and inhibition of protein synthesis was determined. (D) Binding of Fab 13.4.1 and Fab 13.4.1–PE38 to APCs. Competitive binding analysis of the ability of purified recombinant Fab 13.4.1 and Fab 13.4.1–PE38 to inhibit the binding of 125I-labeled Fab 13.4.1 to RMA-S⋅Kk cells loaded with 0.1 mM Ha and NP peptides. Apparent Kd is determined by the concentration of competitor which caused 50% inhibition of the binding of the iodinated Fab 13.4.1.