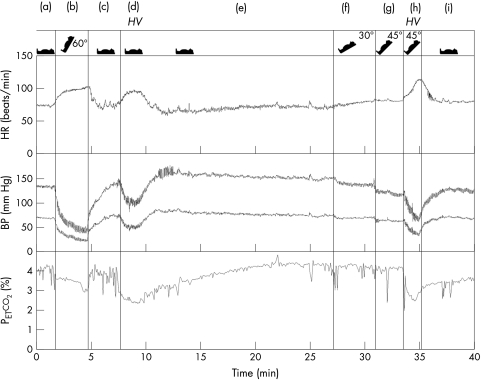
Figure 1 During the tilt table test the patient subsequently underwent the following conditions: supine rest (a), 60° tilt (b), supine rest (c), hyperventilation (d), supine rest (e), 30° tilt (f), 45° tilt (g), 45° tilt + hyperventilation (h), and supine rest (i). Both tilting and hyperventilation caused a significant fall of blood pressure. The vasodepressive effect of hyperventilation added to the hypotensive effect of tilting (condition (h)). BP, finger blood pressure; HR, heart rate; HV, hyperventilation; Petco2, end tidal CO2 tension.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.