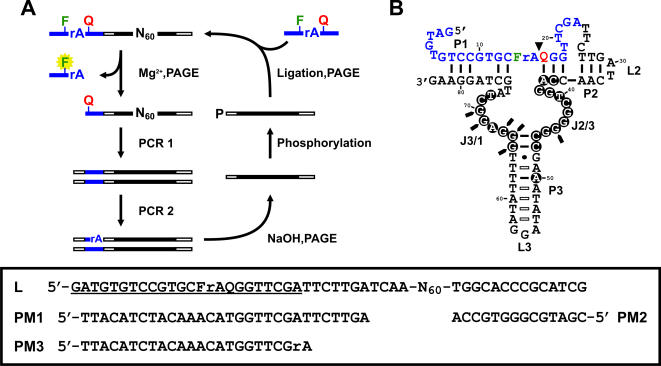
Figure 1.
(A) In vitro selection scheme. The self-cleaving construct of the library consists of a DNA substrate (blue bars), 2 primer binding sites (open bars) and a random library (black bars). The substrate has one ribonucleotide, rA, flanked immediately by a fluorescein (F)- and a DABCYL (Q)-modified deoxyribothymidine. DNA species that are able to self-cleave in the presence of Mg2+ are isolated by denaturing PAGE and subsequently subjected to PCR- amplification. A ribo-linkage (rA) is introduced to the top strand of the PCR product during PCR 2, which enables the recovery of the DNAzyme strand after NaOH treatment followed by PAGE purification. To regenerate the self-cleaving construct, the DNA molecules are phosphorylated at the 5′ ends and ligated to the substrates. The selection cycle continues until a desired cleavage activity is reached. N represents A, G, C or T; P, phosphate. (B) MgZ in cis. Filled circles, absolutely conserved residues; Open bars, covariations; Filled triangle, cleavage site; Filled arrows, DMS methylation interfered residues; F, fluorescein-dT; Q, DABCYL-dT. Inset: random library in the self-cleaving construct (L) and the primers used (PM1-3). Substrate sequence is underlined.