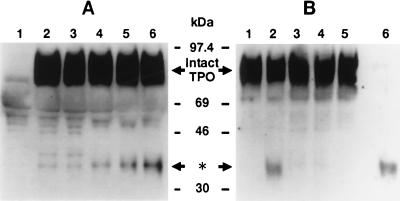
Figure 1.
Cleavage of rhTPO by platelet suspensions. (A) Time course. Platelet pellets were resuspended in a nominally calcium-free modified Hepes⋅Tyrode buffer at a concentration of 3 × 108 platelets per ml. RhTPO (1 μg/ml) and 1 mM calcium ions were or were not added to the platelet suspension, and incubation was conducted for various times at 37°C. The platelets were then lysed by the addition of 2× concentrated SDS/PAGE buffer, and subjected to 7.5–15% gradient SDS/PAGE. Proteins were then electroblotted onto a PVDF membrane, stained by anti-rhTPO Ab, and detected by the ECL method, as described. Prestained protein markers were obtained from Amersham. Lanes: 1, platelet lysate only without exogenous TPO; 2, sample immediately lysed after the addition of rhTPO (1 μg/ml) and 1 mM calcium ions; 3–6, samples lysed 1, 10, 30, and 60 min, respectively, after those additions. The position of the intact rhTPO and the 34-kDa protein band of interest (∗) are indicated by the arrows. (B) The cleavage of rhTPO is inhibited by hirudin and requires calcium ions. Platelets were lysed by the addition of 2× concentrated SDS/PAGE buffer immediately or after incubation for 1 hr at 37°C with rhTPO (1 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of 1 mM calcium ions. Lysed samples were subjected to 7.5–15% gradient SDS/PAGE. RhTPO was detected as described in A. Lanes: 1, immediately lysed sample; 2, 1-hr incubation in the presence of calcium ion (1 mM); 3, 1-hr incubation without the addition of calcium ions; 4, 1-hr incubation with EGTA (1 mM); 5, 1-hr incubation in the presence of calcium ion plus hirudin (10 units per ml); 6, free rhTPO incubated with thrombin (10 units per ml).