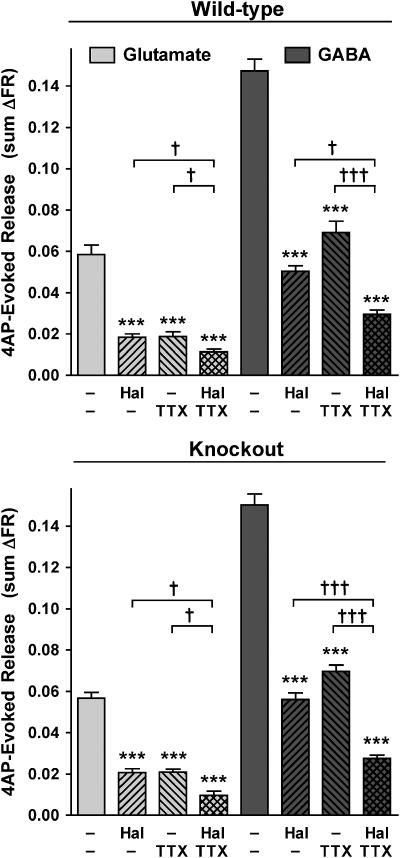
Figure 3.
Halothane inhibits residual tetrodotoxin-insensitive 4AP-evoked glutamate release. At a nearly maximal inhibitory concentration (∼2 times MAC for WT mouse), halothane (Hal) inhibited 4AP-evoked glutamate and GABA release in the presence of a saturating concentration of tetrodotoxin (TTX, 1 μM) in WT (0.71±0.04 mM) and KO (0.75±0.06 mM) mice, compared to halothane (0.76±0.03 and 0.75±0.04 mM, respectively) or tetrodotoxin alone, in the presence of Ca2+. Statistical analysis of mean±s.e.m. values was performed by one-way ANOVA, with Bonferroni post hoc testing between respective control (***P<0.001) and between indicated groups (†P<0.05, †††P<0.001).