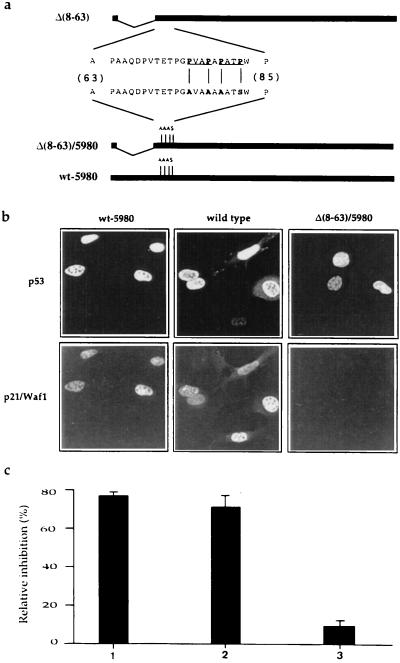
Figure 3.
Structure, p21/Waf1 induction and growth arrest function analysis of proline-rich region mutants. (a) Amino acid sequence of the proline-rich region in mouse p53. The PXXP motifs are underlined; the substituted amino acids in the mutated version are indicated in bold letters. Clone p53wt-5980 codes for a murine p53 bearing four point mutations that substitute Pro-76, -79, and -81 with alanines, and Pro-84 with serine. (b) Proline substitution in the p53 sequence does not interfere with its ability to transactivate endogenous p21/Waf1 as assayed by the induction of the corresponding protein product. Expression plasmids were microinjected in BALB/c (10)1 cells. Six hours later cells were fixed and analyzed for expression of the p53 protein and of endogenous p21/Waf1 by immunofluorescence. p21/Waf1 was detected by anti-peptide antibody as described (29). Wt p53 and Δ(8–63)/5980 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. (c) Analysis of the growth arrest function of p53 wt-5980 (1), wt p53 (2), and Δ(8–3)/5980 (3). BrdUrd incorporation was monitored as described in legend to Fig. 2.