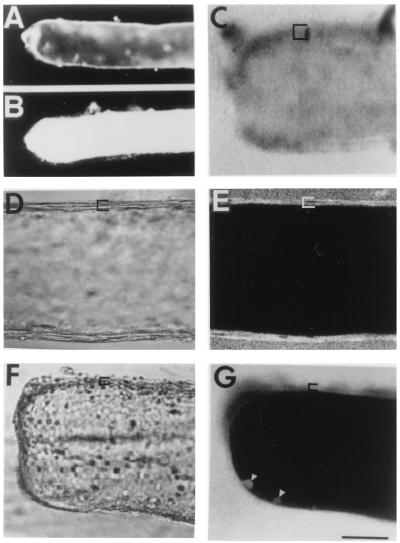
Figure 1.
Dye uptake/exclusion by MGAs. Cut end of transected axons are oriented to the left in all figures. In fluorescent images, black represents lack of fluorescence. In all confocal images using a Zeiss LSM 410, the <5-μm-thick confocal plane is parallel to, and through, the midsection of the long axis of an MGA. Brackets show the extent of glial sheath. (A) Sealed MGA in physiological saline. (B) Unsealed MGA in Ca2+-free saline: fluorescence images where dye-free saline was replaced with 1% pyrene-saline at 60 min postseverance and replaced 15 min later with dye-free saline. (C) Confocal fluorescence image where dye-free, divalent-cation-free saline was replaced at 75 min postseverance with 0.1% FITC–dextran in divalent-cation-free saline for 15 min. [Compare fluorescing axoplasm in this unsealed axon with nonfluorescing axoplasm in confocal images of intact (E) or sealed (G) axons.] (D and E) DIC and confocal fluorescence images of intact MGA maintained in physiological saline for 60 min before adding 0.1% Texas Red–dextran for 45 min. (F and G) DIC and confocal fluorescence images of cut end of MGA where physiological saline was replaced at 75 min postseverance with 0.1% Texas Red–dextran for 15 min. Each line of all confocal images in this and the following paper was built up as the average of 8 line scans. Arrowheads indicate dye-filled vesicles or plasmalemmal invaginations. (Bar = 170 μm for A and B, 60 μm for C–G.)