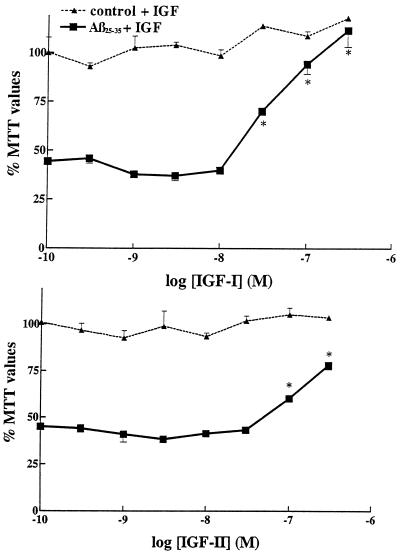
Figure 2.
Neuroprotective effect of IGF-I (Upper) and IGF-II (Lower) against Aβ25–35-induced toxicity in rat primary hippocampal neurons. Aβ25–35 alone (30 μM), induced a marked loss in MTT values down to 44% of controls. Concentration-dependent neuroprotective effects of IGF-I and IGF-II are observed against Aβ25–35 toxicity when the trophic factors are added simultaneously with Aβ25–35. Increasing concentrations of IGFs, by themselves, failed to have significant effects in control cultures (dashed lines). IGF-I was clearly more effective than IGF-II. ∗, P < 0.01 as Aβ-treated neurons.