Figure 7.
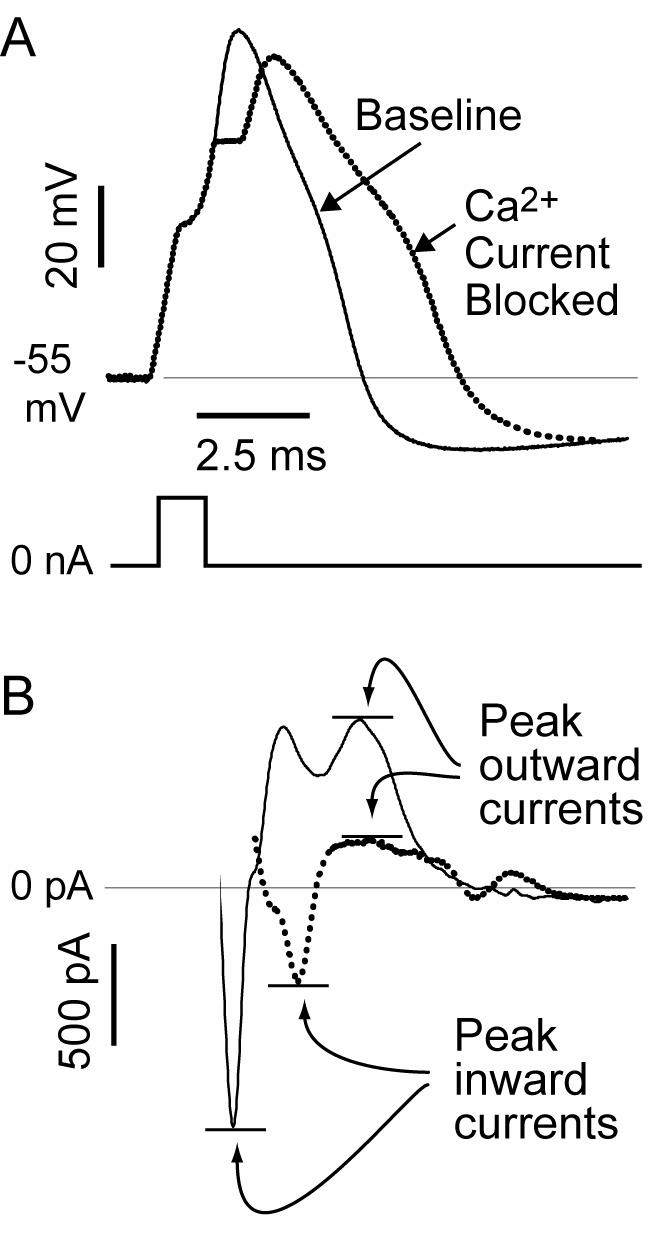
Consequence of loss on Ca2+ current on membrane function. (A) Recordings from a dissociated sensory neuron by the patch-clamp technique show the action potential (AP) voltage traces (top) produced by a current pulse (bottom) at baseline and after Ca2+ current is blocked by selective toxins. (B) Using the baseline AP trace as a voltage command (not shown), the maximal inward component of the total current is reduced, but the later outward current is also diminished, accounting for the prolongation of the AP and diminished afterhyperpolarization evident in the voltage traces. From McCallum et al (48), with permission.
