Figure 1.
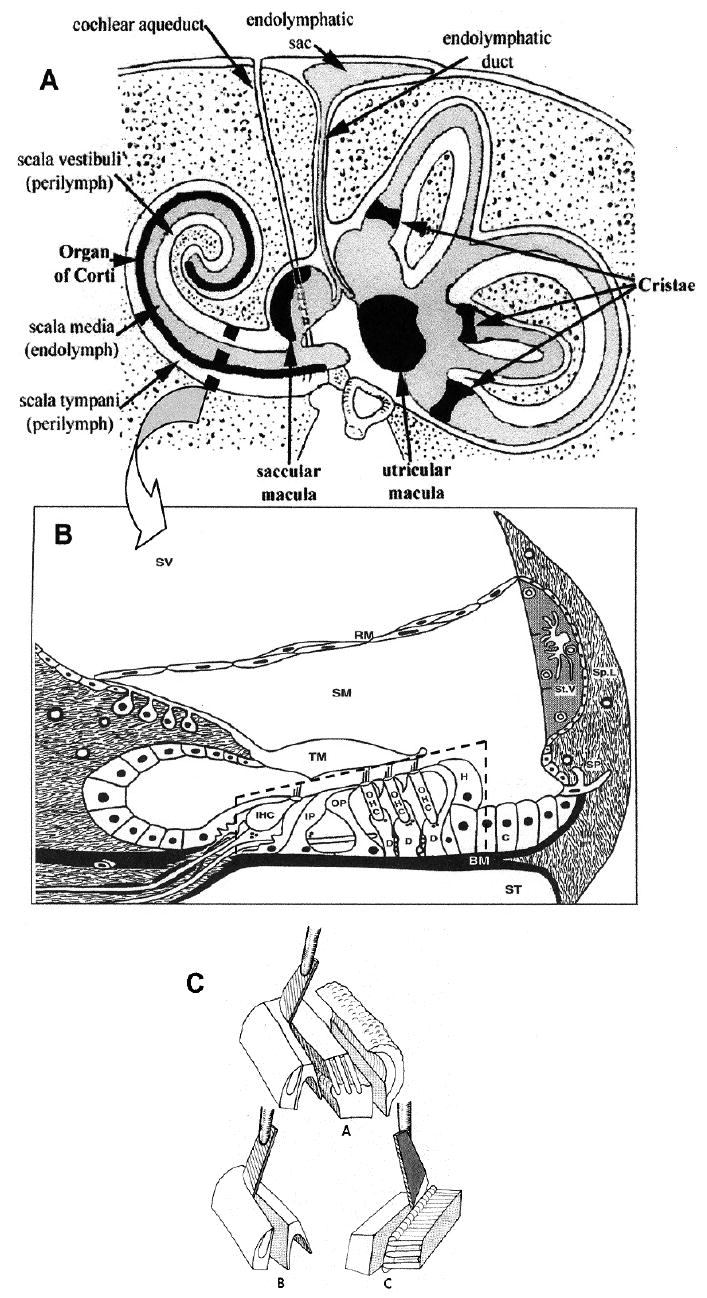
(A) Diagram of the human inner ear and temporal bone in cross-section. Reproduced with permission from [37]. Arrow points to an enlarged diagram of a cross-section of a cochlear turn (B). Organ of Corti (broken-line box) consisting of sensory cells (IHC – inner hair cells; OHC – three rows of outer hair cells) and supporting cells (IP – inner pillar; OP – outer pillar; D – Deiters; H – Hensen; C – Claudius) rests on the basilar membrane (BM), and is covered by the tectorial membrane (TM). There are three fluid compartments: scala vestibuli (SV) and scala tympani (ST), containing perilymph, and scala media (SM) containing endolymph. Reproduced with permission from [38]. (C) Schematic representation of the method for the separation of the organ of Corti into cell layers. A – organ of Corti divided into inner layer (left) and outer layer (middle). B – isolation of inner hair cell layer. C – isolation of outer hair cell layer.
