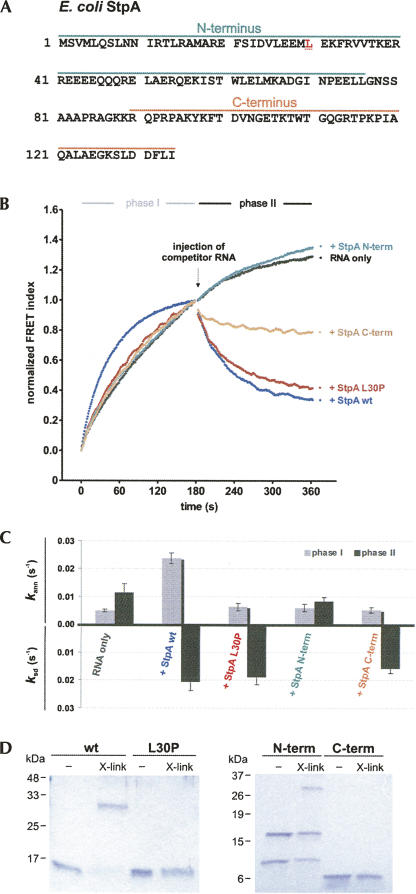
FIGURE 2.
Only dimerization-competent StpA enhances RNA annealing, whereas the ability to facilitate strand displacement resides in the C-terminal domain. (A) The N- and C-terminal domains, as well as the position of the L30P mutation, are indicated in the protein sequence of E. coli StpA. (B) Wild-type StpA (wt), StpA L30P, the N-terminal, and the C-terminal fragment were assayed for their RNA annealing and strand displacement activity as described in the Materials and Methods. (C) Kinetic evaluation of the reactions. Only StpA wt accelerates annealing; StpA wt, StpA L30P, and StpA C-term facilitate strand displacement in phase II. (D) Coomassie blue–stained SDS-polyacrylamide gels showing the analysis of protein–protein cross-link reactions. X-link indicates the incubation with cross-link agents EDC/NHS. The calculated molecular weights of the monomers are as follows: StpA, 15 kDa; StpA L30P, 15 kDa; N-terminal domain, 9 kDa; and C-terminal domain, 5 kDa.