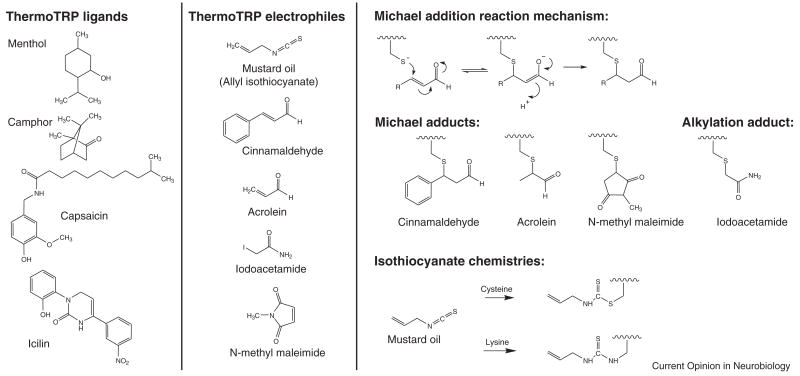
Figure 2.
Left panels: Chemical structures of TRP agonists. Agonists that behave as traditional ligands (left), and also those that covalently modify amino acids (right). Right panel: Electrophilic Michael addition acceptors, such as alpha beta unsaturated aldehydes found in cinnamaldehyde, acrolein, and N-methyl maleimide can form adducts with cysteine residues in proteins using the reaction scheme shown. Below, are the structures of the cysteine adducts formed by the three electrophiles. Alkylating agents such as iodoacetamide may also form cysteine adducts in proteins, producing the structure shown. Isothiocyanate compounds such as allyl isothiocyanate can form adducts with both cysteine and lysine residues in proteins