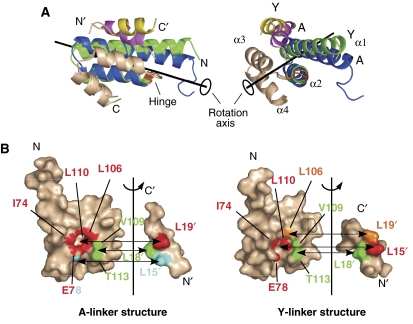
Figure 3.
Detailed comparison of the two crystal structures. (A) Conformational differences between the two Tom20 structures. The two crystal structures were compared using the program DynDom (Hayward and Lee, 2002). The Tom20 structure consists of two domains, α1–α2 (residues 59–99) and α3–α4 (residues 101–126). The α3–α4 domain (white) is superimposed. The α1–α2 domain of the Y-linker structure (green) rotates 10 deg around the axis and moves 0.2 Å along the axis relative to the A-linker structure (blue). The hinge residue was identified as Cys100 (orange). The bound presequence peptide of the A-linker structure is magenta, and that of the Y-linker structure is yellow. (B) Open-book representations of the contact residues at the Tom20–presequence interface. The surface of Tom20 that contacts one of the three leucine residues of the presequence peptide is displayed in the same color. Two atoms are defined as being in contact if the distance is less than 4.0 Å. The buried surface areas are similar: 305±2 Å2 for the A-linker structure versus 338±32 Å2 for the Y-linker structure.