Figure 5. shtd encodes the APC-1 homolog.
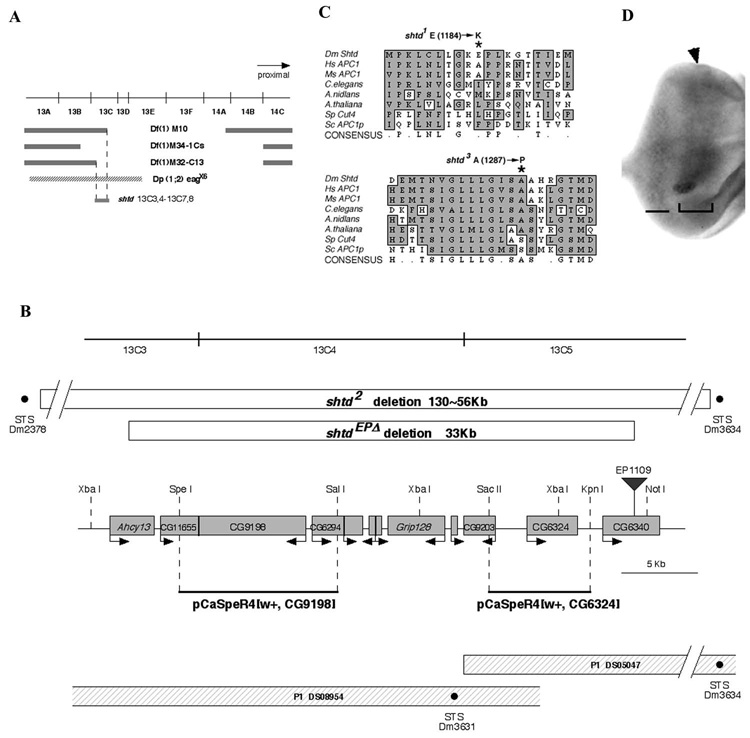
(A) shtd deficiency mapping. Deficiencies uncovering the 13C region and the duplication chromosome Dp(1;2) eagx6 are shown. The shtd gene maps by complementation to 13C3,4-13C7,8. (B) Schematic representation of the shtd locus. An approximately 35 kb region surrounding CG9198 is shown. The shtdEPΔ and shtd² deletions are shown by open boxes; the breakpoints of shtd² fall outside of the range of this map, and the nearest intact STS markers are shown. The insertion site of EP1109, which was used for the imprecise excision, is shown by an inverted triangle. Predicted open reading frames are shown by shaded boxes, with the putative direction of transcription showed by the arrow. P1 clones and STS markers (black dots) are shown at the bottom. For the rescue experiment, genomic fragments were isolated from P1 clones (solid black lines). The genomic fragment that contains the CG9198 ORF rescued shtd mutant phenotype while the fragment that contains the CG6324 did not. The restriction enzyme sites used for subcloning are shown on the map. (C) The shtd¹ allele results from a substitution of lysine for glutamic acid at position 1184 (asterisk). The shtd³ allele results from a substitution of proline for a conserved alanine at position 1287 (asterisk). (D) shtd mRNA expression pattern in third instar eye disc. Expression is higher in the domain surrounding the MF (bracketed region) and posterior portion of eye disc (bar). The arrowhead indicates the MF.
