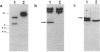Abstract
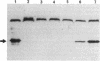
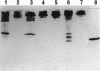
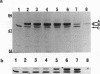
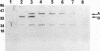
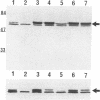
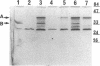
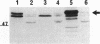
Deletion mutants of Escherichia coli specific for hydrogenase isoenzyme 1 (HYD1) have been constructed and characterized. The hya operon, which contains genes for the two HYD1 structural subunits and four additional genes, was mapped at 22 min on the E. coli chromosome. The total hydrogenase activities of the HYD1-negative mutant and wild-type strains were similar. However, the formate dehydrogenase activity associated with the formate hydrogen lyase pathway was lower in the mutant. The hya mutant (strain AP1), complemented with only the hydrogenase structural genes (hyaAB), produced antigenically identifiable but inactive HYD1 protein. The first five genes of hya (hyaA to hyaE) were required for the synthesis of active HYD1, but wild-type levels of HYD1 activity were restored only when mutant cells were transformed with all six genes of the operon. When AP1 was complemented with hya carried on a high-copy-number plasmid, the HYD1 structural subunits were overexpressed, but the excess protein was unprocessed and localized in the soluble fraction of the cell. The products of hyaDEF are postulated to be involved in the processing of nascent structural subunits (HYAA and HYAB). This processing takes place only after the subunits are inserted into the cell membrane. It is concluded that the biosynthesis of active HYD1 is a complex biochemical process involving the cellular localization and processing of nascent structural subunits, which are in turn dependent on the insertion of nickel into the nascent HYD1 large subunit.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Isolation and characterisation of a soluble active fragment of hydrogenase isoenzyme 2 from the membranes of anaerobically grown Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):277–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Nickel-containing hydrogenase isoenzymes from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):454–459. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.454-459.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkmann A., Böck A. Characterization of a cis regulatory DNA element necessary for formate induction of the formate dehydrogenase gene (fdhF) of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri A., Krasna A. I. Isolation of genes required for hydrogenase synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3289–3298. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Guest J. R. Production of a soluble form of fumarate reductase by multiple gene duplication in Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec;102(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb06263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. M., Garg N., Garg R. P., Tibelius K. H., Yates M. G., Arp D. J., Seefeldt L. C. The identification, characterization, sequencing and mutagenesis of the genes (hupSL) encoding the small and large subunits of the H2-uptake hydrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):999–1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis K., Patel P., Wendt J. C., Shanmugam K. T. Purification and characterization of two forms of hydrogenase isoenzyme 1 from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5750–5757. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5750-5757.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Garoff H., Lehrach H. A subcloning strategy for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5541–5549. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. Molecular cloning of a bovine cathepsin. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):707–712. doi: 10.1042/bj2250707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. M., Aldea M., Washburn B. K., Babitzke P., Kushner S. R. New method for generating deletions and gene replacements in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4617–4622. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4617-4622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Zuber M., Evans H. J. Immunological homology between the membrane-bound uptake hydrogenases of Rhizobium japonicum and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):579–584. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.579-584.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. J., Sawers R. G., Rugman P. A., Boxer D. H., Higgins C. F. Effects of anaerobic regulatory mutations and catabolite repression on regulation of hydrogen metabolism and hydrogenase isoenzyme composition in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):405–411. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.405-411.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc M., Colbeau A., Cauvin B., Vignais P. M. Cloning and sequencing of the genes encoding the large and the small subunits of the H2 uptake hydrogenase (hup) of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):97–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00340186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. H., Patel P., Sankar P., Shanmugam K. T. Isolation and characterization of mutant strains of Escherichia coli altered in H2 metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):344–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.344-352.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J., Przybyla A. E. Cloning, characterization, and sequencing of the genes encoding the large and small subunits of the periplasmic [NiFe]hydrogenase of Desulfovibrio gigas. DNA. 1987 Dec;6(6):539–551. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz S., Jacobi A., Schlensog V., Böhm R., Sawers G., Böck A. Molecular characterization of an operon (hyp) necessary for the activity of the three hydrogenase isoenzymes in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):123–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. L., Stults L. W., Robson R. L., Mortenson L. E. Cloning, sequencing and characterization of the [NiFe]hydrogenase-encoding structural genes (hoxK and hoxG) from Azotobacter vinelandii. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90342-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon N. K., Robbins J., Peck H. D., Jr, Chatelus C. Y., Choi E. S., Przybyla A. E. Cloning and sequencing of a putative Escherichia coli [NiFe] hydrogenase-1 operon containing six open reading frames. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1969–1977. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1969-1977.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Médigue C., Bouché J. P., Hénaut A., Danchin A. Mapping of sequenced genes (700 kbp) in the restriction map of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):169–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Lee J. H., Shanmugam K. T. Cloning of hydrogenase genes and fine structure analysis of an operon essential for H2 metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):353–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.353-360.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Lee J. H., Shanmugam K. T. Gene-product relationships of fhlA and fdv genes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5440–5445. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5440-5445.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankar P., Shanmugam K. T. Biochemical and genetic analysis of hydrogen metabolism in Escherichia coli: the hydB gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5433–5439. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5433-5439.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Ballantine S. P., Boxer D. H. Differential expression of hydrogenase isoenzymes in Escherichia coli K-12: evidence for a third isoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1324–1331. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1324-1331.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G., Boxer D. H. Purification and properties of membrane-bound hydrogenase isoenzyme 1 from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):265–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayavedra-Soto L. A., Powell G. K., Evans H. J., Morris R. O. Nucleotide sequence of the genetic loci encoding subunits of Bradyrhizobium japonicum uptake hydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8395–8399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlensog V., Böck A. Identification and sequence analysis of the gene encoding the transcriptional activator of the formate hydrogenlyase system of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1319–1327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. Regulation and over-expression of the fnr gene of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3279–3288. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker K., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Randomly induced Escherichia coli K-12 Tn5 insertion mutants defective in hydrogenase activity. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):831–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.831-836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker K., Reijnders W. N., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Initial cloning and sequencing of hydHG, an operon homologous to ntrBC and regulating the labile hydrogenase activity in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4448–4456. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4448-4456.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voordouw G., Menon N. K., LeGall J., Choi E. S., Peck H. D., Jr, Przybyla A. E. Analysis and comparison of nucleotide sequences encoding the genes for [NiFe] and [NiFeSe] hydrogenases from Desulfovibrio gigas and Desulfovibrio baculatus. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2894–2899. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2894-2899.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R., Boxer D. H. Pleiotropic hydrogenase mutants of Escherichia coli K12: growth in the presence of nickel can restore hydrogenase activity. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A. Genetic and physiological characterization of new Escherichia coli mutants impaired in hydrogenase activity. Biochimie. 1986 Jan;68(1):167–179. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)81081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Waugh R., Edmonds C. J., Holt S. E., Boxer D. H. Nickel deficiency gives rise to the defective hydrogenase phenotype of hydC and fnr mutants in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1709–1718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]