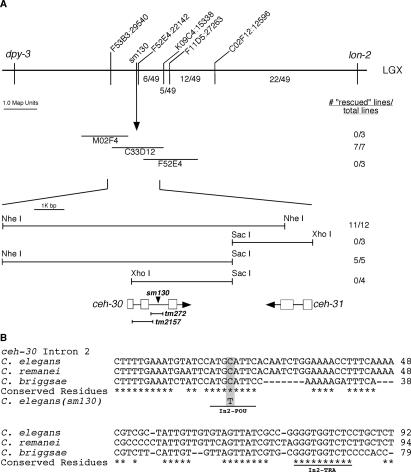
Figure 1.
Mapping and rescue of the sm130 mutant. (A, top panel) The genetic markers and SNPs used to map the sm130 mutation are indicated above the horizontal bar. The numbers below the bar indicate the fraction of 49 recombinants between lon-2 and sm130 that occurred between particular SNP markers. (Middle panel) Cosmids tested for rescue. Transgenic animals carrying the indicated Cosmid DNA as extrachromosomal arrays were generated and scored for rescue of the ectopic CEM death defect in the sm130 mutant as described in Materials and Methods. The number of rescued lines versus total lines generated is indicated to the right. (Bottom panel) Partial restriction map of the rescuing Cosmid C33D12 and the sm130 rescue data observed for several subclones of C33D12. ORFs in this region are indicated with boxes representing exons and lines representing intronic sequences. The position of the sm130 mutation is indicated with an arrowhead. Two deletion alleles (tm272 and tm2157) of ceh-30 and the ceh-30 regions removed by these mutations are represented below the ceh-30 ORF. (B) Alignment of the ceh-30 intron 2 DNA sequences from three related nematode species (C. elegans, C. briggsae, and C. remanei). Conserved residues are indicated by asterisks. The sm130 lesion is highlighted, and two conserved binding sites for POU-type homeodomain proteins (In2-POU) and TRA-1A (In2-TRA) are underlined.