Fig. 1.
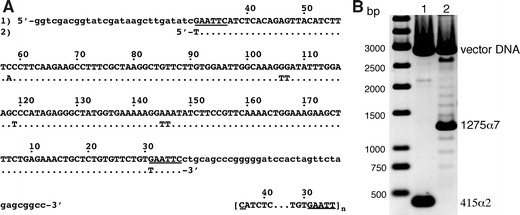
Characterisation of the satellite DNA fragments used for chromatin reconstitutions. a The cloned AGM AS (1) is shown in upper case letters and aligned with the sequence (2) analysed earlier in reconstitutions experiments [adapted from Neubauer et al. 1986]. Lower case letters show flanking vector DNA. The EcoRI recognition sites are underlined. Numbering of sequence positions is according to Rosenberg et al. (1978). The sequence in brackets indicates the repetition of the 172 bp AS monomer starting and ending at the EcoRI site in our case (n = 2, 172-α2 DNA; n = 7, 172-α7 DNA). b Agarose-gel electrophoresis of the AS fragments after separation from the cloning vector with NotI and XhoI (lane1 172-α2, 415 bp, lane 2 172-α7, 1,275 bp). Note, that the target fragments were isolated from agarose gels for the reconstitution experiments. Here, the NotI/XhoI digestion was directly loaded on the gel to also show the occurrence of a distribution of different AS repeat numbers around the major repeat length of n = 7 in the cell line containing pBluescript-KSII-α7
