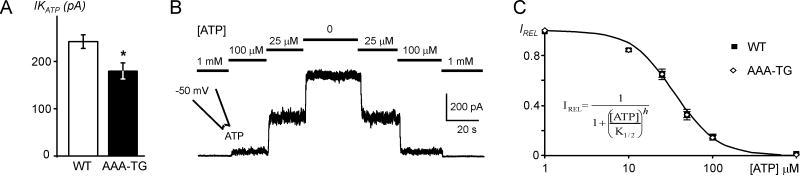
Fig. 6. KATP channels in WT and AAA-TG myocytes.
K+ currents were measured at +50 mV in high symmetrical K+ using excised membrane patches, and KATP current amplitudes calculated as a difference between currents in 0 and 1 mM ATP. A. In AAA-TG myocytes, KATP current density (per patch) is reduced by ∼25% compared to that in WT cells (p<0.01). B. A representative example of an ATP dose-response relationship in WT cells obtained under the same conditions as above. C. Normalized IKATP (IREL) from individual patches were fit with a Hill equation (insert) to estimate the slope (h) and concentration of half maximum block (K1/2). The data at each concentration show only a minor variation, thus standard error (SE) bars are too small compared to symbols. Neither the Hill coefficient (h) nor the sensitivity to ATP (K1/2) are affected in any significant way in AAA-TG myocytes, therefore, for visualization purpose, the averaged data were fit again with the Hill equation and the fit is plotted as indicated (continuous line). n=91 and n=57 for WT and AAA-TG cells, respectively, in all experiments.