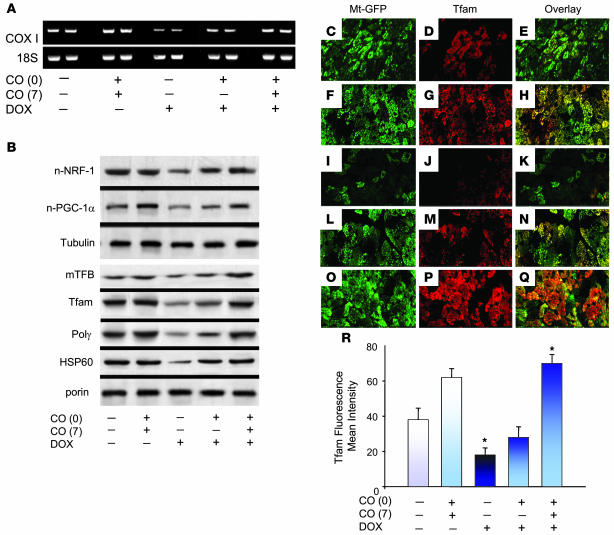
Figure 4. DOX inhibits and CO restores regulation of cardiac mtDNA replication and mitochondrial biogenesis.
(A) Mitochondrial gene expression evaluated by RT-PCR using mouse gene-specific primers for mitochondrial COXI. Nuclear mRNA for 18S rRNA was used to control for RNA integrity and RT-PCR efficiency. (B) Top: Expression of nuclear protein regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis, NRF-1 and PGC-1α, by western blot compared with tubulin. Bottom: Mitochondrial content of regulatory proteins for mtDNA replication by western blot. Mitochondrial mTFB, Tfam, Polγ and HSP-60 are shown compared with porin. DOX effects are reversed by CO. (C–Q) Confocal scanning microscopy of immunolabeling for Tfam (red), mitochondria (green), and overlay in heart tissue. Control sections of LV showed intense Tfam labeling in mitochondria (C–E), and CO did not alter mitochondrial distribution (F–H). (I–K) LV sections of DOX-treated mice. Tfam was clearly labeled in mitochondria of intact but not degenerating or necrotic cardiomyocytes. Also shown are LV sections of mice treated with DOX plus 1 dose of CO (L–N) or DOX plus 2 doses of CO (O–Q). Original magnification, ×300. (R) Histogram of the Tfam fluorescence intensity relative to mitochondrial fluorescence. Values are mean ± SEM of results of 6 mice per group. *P < 0.05 versus other groups.