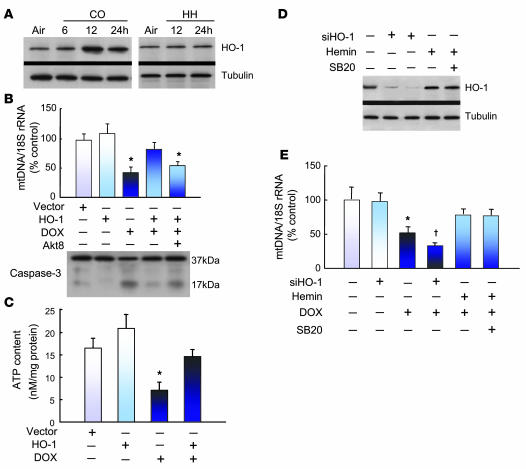
Figure 7. HO-1 protects against DOX-induced mtDNA damage and apoptosis.
(A) Western blots of HO-1 expression before and after CO or HH in control mouse hearts compared with tubulin. (B) Bar graph shows mtDNA copy number measured by real-time PCR relative to nuclear DNA in H9c2 cells before and after HO-1 gene transfer. HO-1 transfection decreased DOX-dependent mtDNA depletion. HO-1–transfected cells treated with the specific Akt inhibitor (Akt8) showed loss of mtDNA protection by HO-1. HO-1 gene transfer also protected H9c2 cells from DOX-induced apoptosis, as shown by western blot analysis with an antibody to both intact and cleaved caspase-3. In HO-1–transfected H9c2 cells preincubated with Akt8, caspase-3 cleavage reemerged (mean ± SEM, n = 3; *P < 0.05 versus untreated cells). (C) Effect of DOX on cellular ATP content and the rescue by HO-1 transfection. *P < 0.05 compared with control and both HO-1 transfection studies. (D) HO-1 silencing in H9c2 cells. Western blot analysis demonstrated loss of HO-1 expression at 24 and 48 hours after HO-1 siRNA. Control cells stimulated with hemin (50 μM) were the positive control. Cells pretreated with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (10 μM) did not show a change in HO-1 protein induction by hemin after an additional 6 hours. (E) mtDNA copy number measured by real-time PCR in H9c2 cells without or with HO-1 silencing. Control or siHO-1 transfected cells were preincubated for 24 hours with DOX alone, with DOX and hemin, or with DOX, hemin, and SB203580. The graphs are means ± SEM for n = 3 per group. *P < 0.05 compared with control; †P < 0.05 compared with DOX alone.