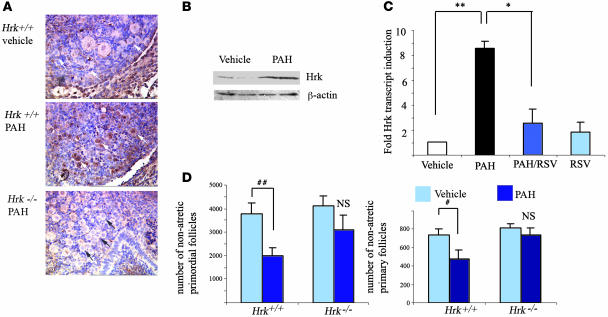
Figure 2. PAH-driven Hrk induction and its functional requirement in regulation of ovarian pool.
(A) Immunohistochemical analysis of Hrk protein (brown staining) in neonatal mouse ovaries following 24 hours of exposure to vehicle or 1 μM DMBA/BaP each during in vitro culture. Induction was observed in oocytes and granulosa cells of both primordial (black and white arrows) and primary follicles. Magnification, ×400. Hrk-deficient ovaries did not show upregulation of immunoreactivity in oocytes after PAH exposure, confirming the specificity of antibody. (B) Western blot analysis of neonate ovaries under the same conditions as described above. Upon adjustment to β-actin ratio, Hrk protein, migrating at approximately 15 kDa, was induced approximately 2.5-fold (P = 0.03). (C) Induction of Hrk transcript in in vitro–treated neonatal ovaries 24 hours after exposure to vehicle, 1 μM DMBA/BaP each (PAHs), treatment with PAH and 2 μM resveratrol (PAH/RSV), or 2 μM resveratrol alone (RSV). The expression data are shown as mean ± SEM of fold change in comparison with the vehicle-treated group and were obtained from 5 sets of independent ovaries per treatment. PAH induced significant (**P = 0.0006) upregulation of Hrk transcript, which was repressed by resveratrol treatment (*P = 0.005). RSV or RSV/PAH groups were not significantly different from vehicle-treated ovaries. (D) Ovaries from Hrk-deficient females were protected from PAH-induced depletion of primordial and primary follicles. Numerical representation of morphometric analysis of ovarian pool for nonapoptotic oocyte-containing primordial (resting) and primary (growing) follicles in sibling offspring born to heterozygote mothers exposed to PAHs prior to pregnancy and during lactation. Data are expressed as mean number of primordial and primary follicles ± SEM. Each genotype group represents combined data of offspring born to mothers exposed to vehicle (Hrk+/+, n = 5; Hrk–/–, n = 7) or treated with PAH (Hrk+/+, n = 4; Hrk–/–, n = 5). A significant reduction of follicles was only observed in the wild-type ovaries (#P = 0.03; ##P = 0.05; NS, not significantly different).