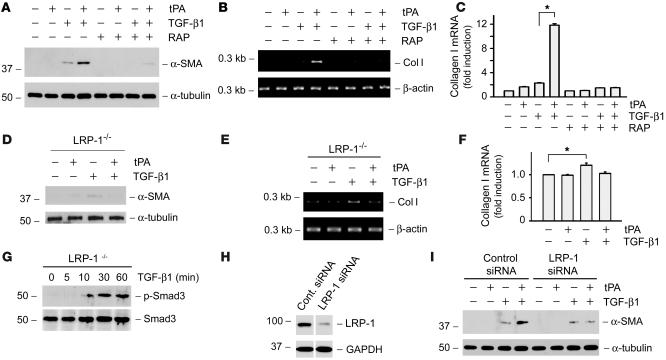
Figure 3. LRP-1 receptor is required for tPA to elicit its fibrogenic action.
(A–C) The RAP, an antagonist of LRP-1, abolished the effect of tPA on myofibroblast activation. The synergistic effect of tPA on α-SMA (A) and type I collagen (B and C) induction was abrogated in the presence of RAP (0.5 μM) in NRK-49F cells. (D–F) Ablation of LRP-1 abolished the effect of tPA on myofibroblast activation. tPA failed to promote TGF-β1–induced α-SMA (D) and type I collagen (E and F) expression in LRP-1–deficient PEA-13 fibroblasts. tPA, 10–8 M; TGF-β1, 0.5 ng/ml. Quantitative presentation of type I collagen mRNA levels in different groups is given in C and F. *P < 0.05. (G) TGF-β1 induced Smad3 phosphorylation and activation in LRP-1–deficient PEA-13 cells. Cell lysates were prepared at different time points after stimulation with TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml) and immunoblotted with antibodies against phospho-specific and total Smad3. (H and I) Knockdown of LRP-1 in NRK-49F cells abolished the synergistic effect of tPA. (H) Western blot analysis demonstrated the downregulation of LRP-1 in NRK-49F cells after transfection of the LRP-1–specific siRNA. The lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous. (I) Downregulation of LRP-1 in NRK-49F cells abolished the α-SMA expression induced by tPA (10–8 M), but not TGF-β1 (0.5 ng/ml).