Figure 5.
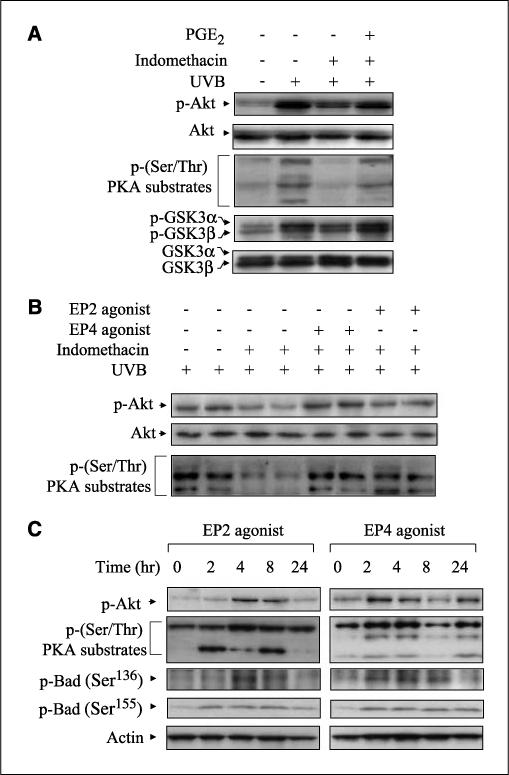
Effects of PGE2, EP2, and EP4 agonists on the activation of Akt and PKA. A, CD-1 mice were pretreated topically with 50 μg indomethacin 30 min before exposure of 5.0 kJ/m2 UVB and posttreated topically with 5 μg PGE2 30 min after exposure. The animals were sacrificed 24 h following UVB exposure, and protein extracts (50−100 μg) were electrophoresed. Specified bands were detected by immunoblotting, and total Akt and total GSK3α/β served as internal controls. B, CD-1 mice were pretreated topically with 50 μg indomethacin 30 min before UVB (5.0 kJ/m2) exposure and posttreated topically with 25 μg of EP2 or EP4 agonist 30 min after exposure. The mice were sacrificed 24 h after exposure, and total protein was isolated from the dorsal skin. After electrophoresis, the membranes were probed with antibodies for p-Akt and p-(Ser/Thr) PKA substrates. Each lane represents an individual mouse. C, EP agonists (25 μmol) were applied to the backs of CD-1 mice. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated times, and total protein was isolated from the dorsal skin. Membranes were probed using antibodies for p-Akt, p-PKA substrates, and p-Bad (Ser136 and Ser155). In (A) to (C), two mice were used per experiment, and the data are representative of two independent experiments.
