Figure 4. S. aureus ΔhssR and ΔhrtA exhibit liver-specific hypervirulence.
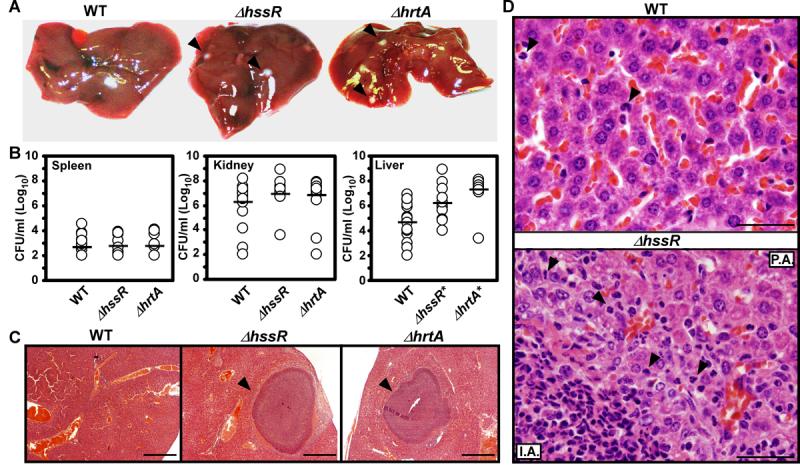
A) Photographs of livers dissected from BALB/c mice infected with wildtype and ΔhssR or ΔhrtA (1 × 106 CFUs for all strains) 96 hours post infection. Arrowheads mark ΔhssR and ΔhrtA-induced hepatic abscesses. Photographs are representative of all livers analyzed. Abscesses were visible in virtually all livers from ΔhssR and ΔhrtA infected mice, while none were found in wildtype infected mice. B) S. aureus multiplication in infected mouse organs as measured by tissue homogenization, dilution, and colony formation on agar media 96 hours post infection. Each symbol represents data from one infected animal. The limit of detection in these experiments is 100 CFUs. The horizontal line denotes the mean of the log and the asterisks denote statistically significant differences from wildtype as determined by Student's t test (p≤0.05). C) Representative Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining of liver sections infected with WT, ΔhrtA, or ΔhssR strains at 40X magnification. Arrowheads mark ΔhssR- and ΔhrtA-induced hepatic abscesses. D) Representative H&E staining of liver sections infected with WT or ΔhssR strains at 1,000X magnification. Arrowheads mark PMNs in the tissues. P.A; proximal to the abscess and I.A; inside the abscess.
