Figure 5. Infection with S. aureus ΔhssR or ΔhrtA inhibits innate immune responses.
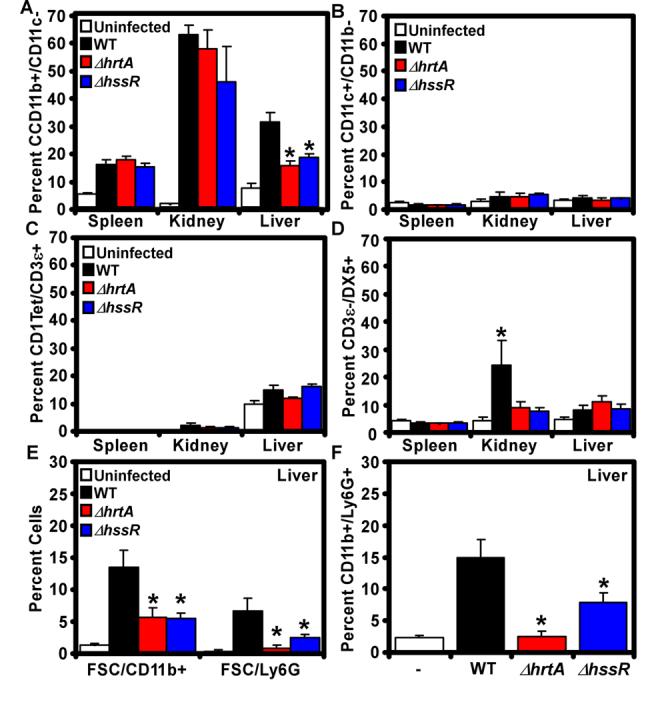
BALB/c animals were left uninfected or infected with wildtype, ΔhssR or ΔhrtA. Four days postinfection (A-D) or two days post infection (E-F) organs were dissected, homogenized, and the infiltration of the indicated immune cells was determined by multiparametric FACS analysis as described in Experimental Procedures. Isolated cells were stained for the detection of: A) phagocytes (B220−/CD11b+/CD11c−), B) dendritic cells (D11c+/CD11b−), C) invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT: CD1 Tetramer (tet)+/B220−/CD3ε+), D) natural killer cells (DX5+/B220−/CD3ε−), E) large CD11b+ and Ly6G+ cells (FSC/CD11b+ and FSC/Ly6G+), and F) granulocytes (B220−/CD11b+/Ly6G+). Results represent the mean ± S.E. from at least three independent animals. Asterisks denote a statistically significant reduction in the detected cells compared to animals infected with the wildtype strain as determined by Student's t test (p<0.05).
