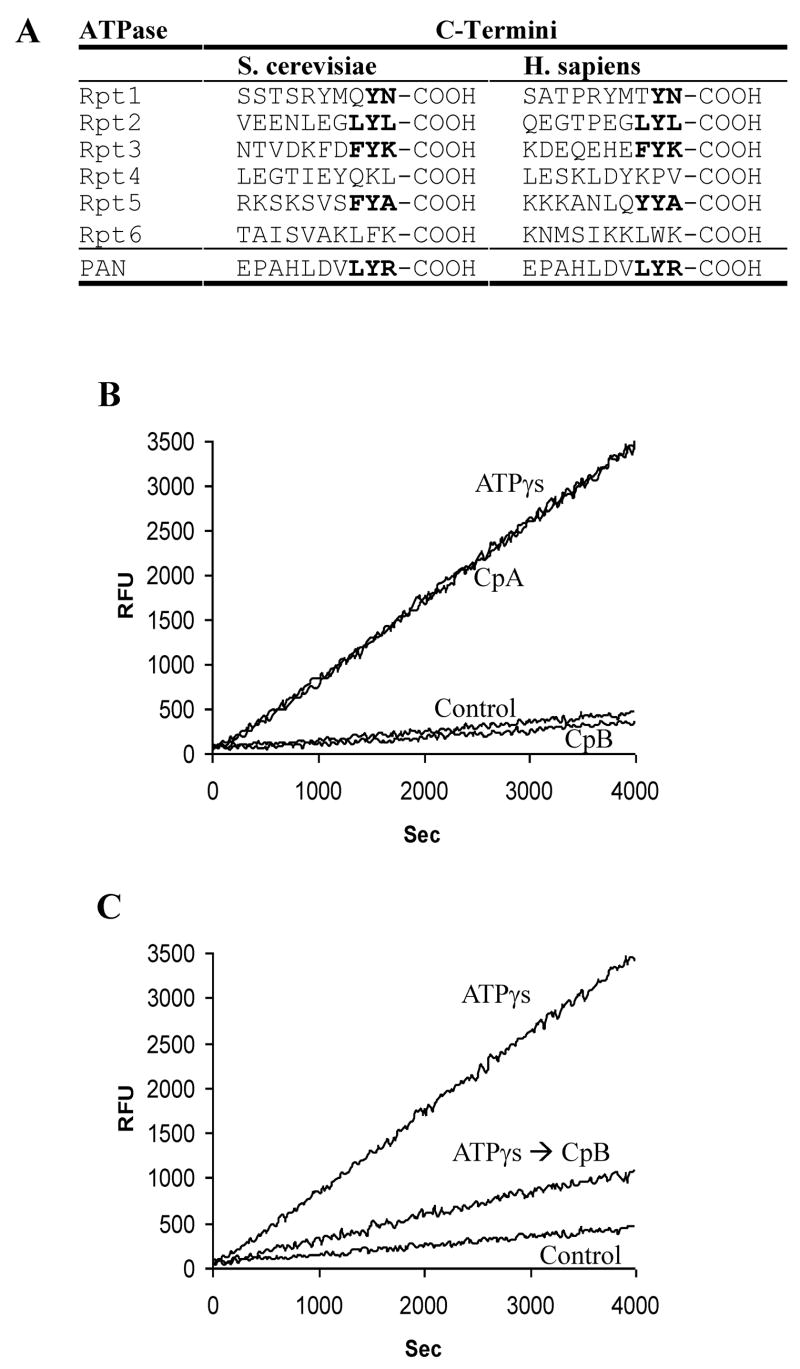
Figure 1.
A) Carboxypeptidase treatment of the proteasomal ATPase regulatory complexes’ eliminates their ability to stimulate the 20S for peptide hydrolysis. A) Two residues preceding the C-terminal arginine in PAN are conserved in the eukaryotic 19S proteasome-regulatory ATPases. B) A solution of PAN, 20S and the fluorescent peptide LFP (Mca-AKVYPYPME-Dpa-amide) was pre-incubated with Carboxypeptidase A (CpA), B (CpB) or without either carboxypeptidase (control and ATPγS) for 5 minutes followed by addition of a general Carboxypeptidase inhibitor from potato tuber, (0.01mg/ml). H2O (Control), or ATPγS (ATPγS, CpA, CpB) was added, and the rate of LFP hydrolysis monitored in real-time. Both CpA and CpB were used at a final concentration of 0.08 Units/ml. C) Same as in A except ATPγS was added prior to addition of CpB. Values are mean’s of three independent experiments, error bars indicate standard deviations and all of these experiment were performed at least three times with similar results.