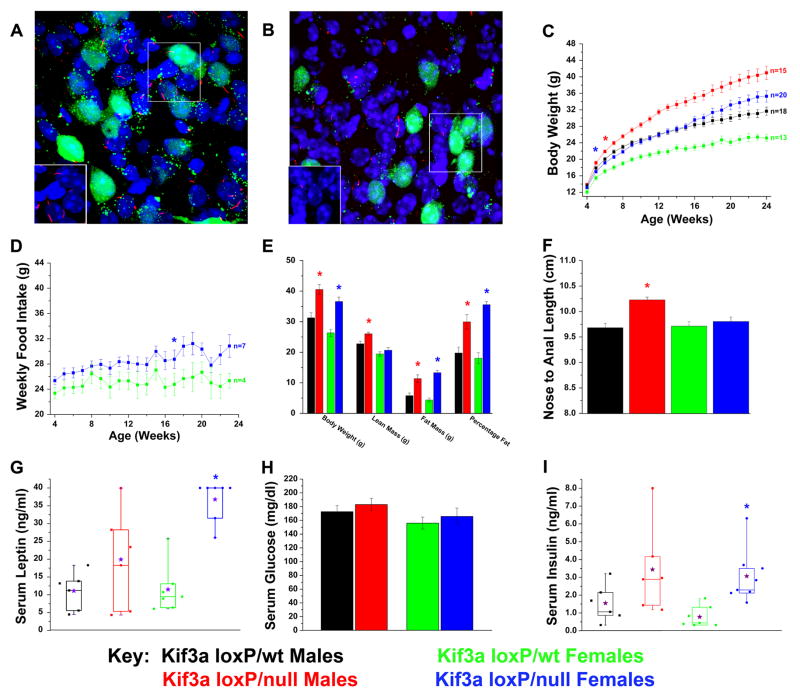
Figure 5. Conditional deletion of Kif3a from POMC-expressing cells in mice leads to increases in weight, adiposity, and body length.
(A, B) Confocal immunofluorescence analysis of (A) Kif3aloxP/wt (Kif3a-pomcWT) and (B) Kif3aloxP/null (Kif3a-pomcKO) arcuate nucleus (100x) bred onto the Z/EG Cre reporter line in the presence of the POMC-cre deletor strain demonstrates the loss or stunting of neuronal cilia (red) on affected POMC neurons (green). Inserts show cilia (red) without the GFP signal and are derived from the boxed region in the image. Note that cilia are still retained on the non-POMC expressing cells in the hypothalamus. (C) Body weight analysis of Kif3a-pomcKO and Kif3a-pomcWT males and females. (D) Weekly food intake of Kif3a-pomcKO females was consistently increased from their Kif3a-pomcWT controls. (E) DXA analysis performed on adult (age 22–25 weeks) mice showed significant increases in fat mass and percentage fat in both sexes, and lean mass in male Kif3a-pomcKO mice. Body weight was measured after the DXA analysis. (F) Nose-to-anal length analysis conducted in anesthetized adult (age 22–25 weeks) Kif3a-pomcWT and Kif3a-pomcKO mice. The average length from independently determined two blinded measurements was used. (G–I) Serum analysis of (G) non-fasted leptin, (H) four-hour fasted glucose, and (I) non-fasted insulin in Kif3a-pomcWT and Kif3a-pomcKO mice (* = p≤0.05, in (C) and (D) indicating the initial point of significant deviation between controls and mutants. The purple stars in G and I represent the means of the individual groups.