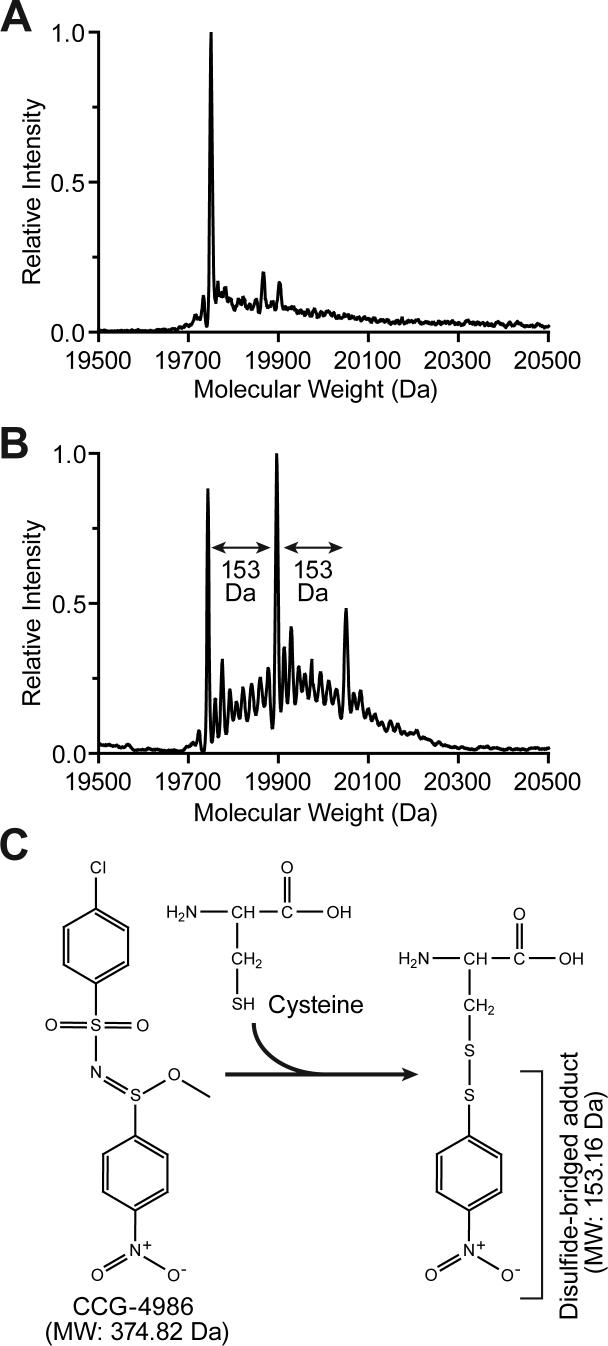
Fig. 5.
Intact molecular weight determination of unreacted and CCG-4986 treated RGS4. (A) Untreated RGS4 was found to exist in a single dominant form corresponding to its predicted molecular weight. (B) RGS4 preincubated with CCG-4986 was found in to consist of three major forms. The three peaks obtained by nano-ESI-MS correspond to the molecular weight of RGS4 (19,743 Da), RGS4 + 153 Da (19,896 Da), and RGS4 + 2×(153 Da) (20,050 Da). (C) CCG-4986 (methyl-N-[(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfinimidoate) has two sulfur atoms that potentially could react with thiol groups of solvent-exposed cysteine residues. Based on the mass spectrometry data from CCG-4986-treated RGS4, we propose that the 4-nitrobenzenethiol group is covalently attached to the two surface-exposed cysteines Cys-71 and Cys-132 in RGS4. The mass of the disulfide-bonded adduct derived from CCG-4986 would correspond precisely with the MS peaks at 19,896 Da (RGS4 + one 4-nitrobenzenethiol group) and 20,050 Da (RGS4 + two 4-nitrobenzenethiol groups).