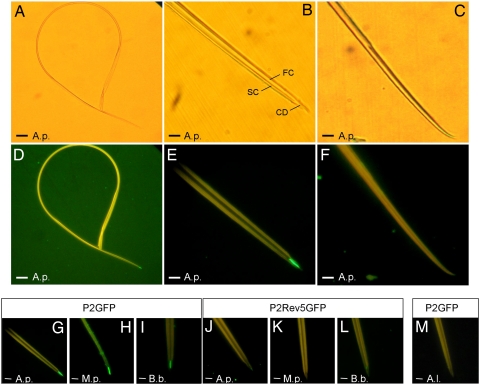
Fig. 2.
In vitro interaction assay between dissected aphid stylets and P2-GFP. (A–F) Stylets incubated with P2-GFP were observed with bright-field (A–C) or epifluorescence (D–F) microscopy to detect bound P2-GFP. The food (FC) and salivary (SC) canals and the common duct (CD) are indicated in B. Images of the entire stylets (A and D) show that P2-GFP binds exclusively to the maxillary stylet tips. Higher magnification reveals that P2 label is restricted to the food/salivary common duct of the maxillary stylets (B and E). The mandibular stylets (C and F) are never labeled. (G–M) Specificity of the interaction between P2-GFP and maxillary stylets. P2-GFP binds to maxillary stylets from vector species A. pisum (A.p.), M. persicae (M.p.), and B. brassicae (B.b.) (G–I), whereas P2Rev5-GFP, a fusion with a nontransmissible P2 mutant, does not (J–L). (M) The non-vector A. lactucae does not bind P2-GFP. (Scale bars: 25 μm in A and D and 5 μm in B, C, and E–M.)