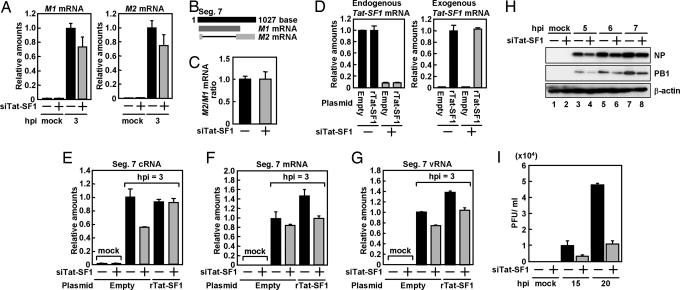
Fig. 2.
Effect of Tat-SF1 knockdown on virus infection. (A) Total RNA was prepared from HeLa cells transfected with control siRNA or siTat-SF1 and superinfected with influenza virus. Real-time RT-PCR was carried out with primer sets specific for M1 mRNA, M2 mRNA, and β-actin mRNA. (B) Representation of M1 and M2 mRNA generated from segment 7. (C) The ratio of the amount of M2 mRNA to that of M1 mRNA in HeLa cells transfected with control siRNA or siTat-SF1 and those infected with influenza virus. (D–G) HeLa cells were transfected with control siRNA or siTat-SF1. At 72 hpt, cells were transfected with pCAGGS-FLAG-rTat-SF1 and pCAGGS-empty plasmids. After 24-h incubation, cells were superinfected with influenza virus. Total RNA was prepared from cells at 3 h postinfection (hpi). Real-time RT-PCR was carried out with primer sets specific for endogenous Tat-SF1 (D Left), exogenous FLAG-rTat-SF1 (D Right), segment 7 RNAs (E, cRNA; F, mRNA; G, vRNA), and β-actin mRNA. The results are normalized as the ratio to the level of β-actin mRNA. Error bars show standard deviation. (H) Western blot analyses of viral proteins. Mock- (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7) or siTat-SF1 siRNA-transfected (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8) HeLa cells were infected with influenza virus at an moi of 5. Western blot analyses were carried with anti-NP, -PB1, or -β-actin antibodies. (I) Single-step virus growth. Mock- or siTat-SF1 siRNA-transfected HeLa cells were infected with influenza virus at an moi of 0.1. Virus titer was examined by plaque assay at the indicated times after infection.